Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
उत्तर
Given:
Frequency of whistle \[f_0 = 1250 \text { Hz }\]
Velocity of car \[v_s\] = 72 kmh−1 =\[72 \times \frac{5}{18} = 20 {\text { ms }}^{- 1}\]
Speed of sound in air v = 340 ms−1
(a) When the car is approaching the person:
Frequency of sound heard by the person \[\left( f_1 \right)\] is given by :
\[f_1 = \left( \frac{v}{v - v_s} \right) \times f_0 \]
On substituting the given values in the above equation, we have:
\[f_1 = \frac{340}{340 - 20} \times 1250\]
\[ = 1328 \text { Hz }\]
(b) When the person is behind the car:
Frequency of sound heard by the person \[\left( f_2 \right)\] is given by :
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{v}{v + v_s} \right) \times f_0\]
On substituting the given values in the above equation, we have :
\[f_2 = \left( \frac{340}{340 + 20} \right) \times 1250\]
\[ = \frac{340}{360} \times 1250 = 1181 \text{ Hz }\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cork floating in a calm pond executes simple harmonic motion of frequency
\[\nu\] when a wave generated by a boat passes by it. The frequency of the wave is
A wave pulse passing on a string with a speed of 40 cm s−1 in the negative x-direction has its maximum at x = 0 at t = 0. Where will this maximum be located at t = 5 s?
Two particles A and B have a phase difference of π when a sine wave passes through the region.
(a) A oscillates at half the frequency of B.
(b) A and B move in opposite directions.
(c) A and B must be separated by half of the wavelength.
(d) The displacements at A and B have equal magnitudes.
A string of linear mass density 0⋅5 g cm−1 and a total length 30 cm is tied to a fixed wall at one end and to a frictionless ring at the other end (See figure). The ring can move on a vertical rod. A wave pulse is produced on the string which moves towards the ring at a speed of 20 cm s−1. The pulse is symmetric about its maximum which is located at a distance of 20 cm from the end joined to the ring. (a) Assuming that the wave is reflected from the ends without loss of energy, find the time taken by the string to region its shape. (b) The shape of the string changes periodically with time. Find this time period. (c) What is the tension in the string?
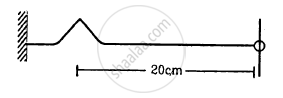
The speed of sound in a medium depends on
At a prayer meeting, the disciples sing JAI-RAM JAI-RAM. The sound amplified by a loudspeaker comes back after reflection from a building at a distance of 80 m from the meeting. What maximum time interval can be kept between one JAI-RAM and the next JAI-RAM so that the echo does not disturb a listener sitting in the meeting. Speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
Two audio speakers are kept some distance apart and are driven by the same amplifier system. A person is sitting at a place 6.0 m from one of the speakers and 6.4 m from the other. If the sound signal is continuously varied from 500 Hz to 5000 Hz, what are the frequencies for which there is a destructive interference at the place of the listener? Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
Find the fundamental, first overtone and second overtone frequencies of an open organ pipe of length 20 cm. Speed of sound in air is 340 ms−1.
An open organ pipe has a length of 5 cm. (a) Find the fundamental frequency of vibration of this pipe. (b) What is the highest harmonic of such a tube that is in the audible range? Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the audible range is 20-20,000 Hz.
An electronically driven loudspeaker is placed near the open end of a resonance column apparatus. The length of air column in the tube is 80 cm. The frequency of the loudspeaker can be varied between 20 Hz and 2 kHz. Find the frequencies at which the column will resonate. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A 30.0-cm-long wire having a mass of 10.0 g is fixed at the two ends and is vibrated in its fundamental mode. A 50.0-cm-long closed organ pipe, placed with its open end near the wire, is set up into resonance in its fundamental mode by the vibrating wire. Find the tension in the wire. Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A Kundt's tube apparatus has a copper rod of length 1.0 m clamped at 25 cm from one of the ends. The tube contains air in which the speed of sound is 340 m s−1. The powder collects in heaps separated by a distance of 5.0 cm. Find the speed of sound waves in copper.
A bullet passes past a person at a speed of 220 m s−1. Find the fractional change in the frequency of the whistling sound heard by the person as the bullet crosses the person. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
Two identical tuning forks vibrating at the same frequency 256 Hz are kept fixed at some distance apart. A listener runs between the forks at a speed of 3.0m s−1 so that he approaches one tuning fork and recedes from the other figure. Find the beat frequency observed by the listener. Speed of sound in air = 332 m s−1.
Two trains are travelling towards each other both at a speed of 90 km h−1. If one of the trains sounds a whistle at 500 Hz, what will be the apparent frequency heard in the other train? Speed of sound in air = 350 m s−1.
An operator sitting in his base camp sends a sound signal of frequency 400 Hz. The signal is reflected back from a car moving towards him. The frequency of the reflected sound is found to be 410 Hz. Find the speed of the car. Speed of sound in air = 324 m s−1
Two sources of sound are separated by a distance of 4 m. They both emit sound with the same amplitude and frequency (330 Hz), but they are 180° out of phase. At what points between the two sources, will the sound intensity be maximum?
Change in temperature of the medium changes ______.
