Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
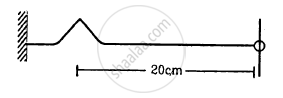
A string of linear mass density 0⋅5 g cm−1 and a total length 30 cm is tied to a fixed wall at one end and to a frictionless ring at the other end (See figure). The ring can move on a vertical rod. A wave pulse is produced on the string which moves towards the ring at a speed of 20 cm s−1. The pulse is symmetric about its maximum which is located at a distance of 20 cm from the end joined to the ring. (a) Assuming that the wave is reflected from the ends without loss of energy, find the time taken by the string to region its shape. (b) The shape of the string changes periodically with time. Find this time period. (c) What is the tension in the string?
उत्तर
Given,
Linear mass density of the string = 0.5 gcm−1
Total length of the string = 30 cm
Speed of the wave pulse = 20 cms−1
The crest reflects the crest here because the wave is travelling from a denser medium to a rarer medium.
Phase change = 0
(a)
Total distance, S = 20 + 20 = 40 cm
Wave speed, \nu = 20 m/s
Time taken to regain shape:
\[Time = \frac{S}{\nu} = \frac{40}{20} = 2 s\]
(b) The wave regain its shape after covering a period distance
\[= 2 \times 30 = 60\] cm
\[\therefore \text{ Time period } = \frac{60}{20} = 3 s\]
(c) Frequency,
\[n = \frac{1}{\text{ Time period}} = \frac{1}{3} s^{- 1}\]
We know:
\[n = \frac{1}{2l}\sqrt{\left( \frac{T}{m} \right)}\]
Here, T is the tension in the string.
Now,
\[m = \text{ Mass per unit length } \]
\[ = 0 . 5 gm/cm\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{3} = \frac{1}{\left( 2 \times 30 \right)} \sqrt{\left( \frac{T}{0 . 5} \right)}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = 400 \times 0 . 5\]
\[ = 200 \text{ dyn }\]
\[ = 2 \times {10}^{- 3} N\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cork floating in a calm pond executes simple harmonic motion of frequency
\[\nu\] when a wave generated by a boat passes by it. The frequency of the wave is
Two periodic waves of amplitudes A1 and A2 pass thorough a region. If A1 > A2, the difference in the maximum and minimum resultant amplitude possible is
A wave pulse passing on a string with a speed of 40 cm s−1 in the negative x-direction has its maximum at x = 0 at t = 0. Where will this maximum be located at t = 5 s?
following Figure shows a wave pulse at t = 0. The pulse moves to the right with a speed of 10 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 1 s, 2 s and 3 s.
A wave is represented by the equation
\[y = \left( 0 \text{ cdot 001 mm }\right) \sin\left[ \left( 50 s^{- 1} \right)t + \left( 2 \cdot 0 m^{- 1} \right)x \right]\]
(a) The wave velocity = 100 m s−1.
(b) The wavelength = 2⋅0 m.
(c) The frequency = 25/π Hz.
(d) The amplitude = 0⋅001 mm.
A wave is described by the equation \[y = \left( 1 \cdot 0 mm \right) \sin \pi\left( \frac{x}{2 \cdot 0 cm} - \frac{t}{0 \cdot 01 s} \right) .\]
(a) Find the time period and the wavelength? (b) Write the equation for the velocity of the particles. Find the speed of the particle at x = 1⋅0 cm at time t = 0⋅01 s. (c) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 3⋅0 cm, 5⋅0 cm and 7⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅01 s?
(d) What are the speeds of the particles at x = 1⋅0 cm at t = 0⋅011, 0⋅012, and 0⋅013 s?
The speed of sound in a medium depends on
At a prayer meeting, the disciples sing JAI-RAM JAI-RAM. The sound amplified by a loudspeaker comes back after reflection from a building at a distance of 80 m from the meeting. What maximum time interval can be kept between one JAI-RAM and the next JAI-RAM so that the echo does not disturb a listener sitting in the meeting. Speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
Calculate the speed of sound in oxygen from the following data. The mass of 22.4 litre of oxygen at STP (T = 273 K and p = 1.0 × 105 N m−2) is 32 g, the molar heat capacity of oxygen at constant volume is Cv = 2.5 R and that at constant pressure is Cp = 3.5 R.
In Quincke's experiment the sound detected is changed from a maximum to a minimum when the sliding tube is moved through a distance of 2.50 cm. Find the frequency of sound if the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
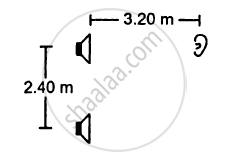
Two stereo speakers are separated by a distance of 2.40 m. A person stands at a distance of 3.20 m directly in front of one of the speakers as shown in figure. Find the frequencies in the audible range (20-2000 Hz) for which the listener will hear a minimum sound intensity. Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
Find the fundamental, first overtone and second overtone frequencies of an open organ pipe of length 20 cm. Speed of sound in air is 340 ms−1.
In a resonance column experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 400 Hz is used. The first resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 20.0 cm and the second resonance is observed when the air column has a length of 62.0 cm. (a) Find the speed of sound in air. (b) How much distance above the open end does the pressure node form?
An open organ pipe has a length of 5 cm. (a) Find the fundamental frequency of vibration of this pipe. (b) What is the highest harmonic of such a tube that is in the audible range? Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1 and the audible range is 20-20,000 Hz.
A U-tube having unequal arm-lengths has water in it. A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz can set up the air in the shorter arm in its fundamental mode of vibration and the same tuning fork can set up the air in the longer arm in its first overtone vibration. Find the length of the air columns. Neglect any end effect and assume that the speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 5 beats per second with another tuning fork which can cause a closed organ pipe of length 40 cm to vibrate in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the first tuning fork is slightly loaded with wax. Find its original frequency. The speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
An operator sitting in his base camp sends a sound signal of frequency 400 Hz. The signal is reflected back from a car moving towards him. The frequency of the reflected sound is found to be 410 Hz. Find the speed of the car. Speed of sound in air = 324 m s−1
A wave of frequency 500 Hz is traveling with a speed of 350 m/s. (a) What is the phase difference between two displacements at a certain point at times 1.0 ms apart? (b) what will be the smallest distance between two points which are 45° out of phase at an instant of time?
