Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
following Figure shows a wave pulse at t = 0. The pulse moves to the right with a speed of 10 cm s−1. Sketch the shape of the string at t = 1 s, 2 s and 3 s.
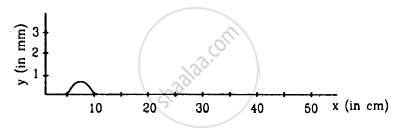
उत्तर
Given,
Wave pulse at t = 0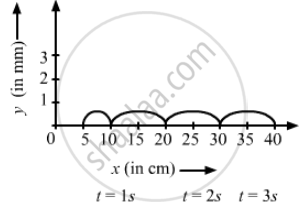
Wave speed = 10 cms−1
Using the formula
\[s = v \times t\]
\[At: \]
\[t = 1 s, s_1 = \nu \times t = 10 \times 1 = 10 cm\]
\[t = 2 s, s_2 = \nu \times t = 10 \times 2 = 20 cm\]
\[t = 3 s, s_3 = \nu \times t = 10 \times 3 = 30 cm\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two waves represented by \[y = a\sin\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] and \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] \[y = a\cos\left( \omega t - kx \right)\] are superposed. The resultant wave will have an amplitude
Two particles A and B have a phase difference of π when a sine wave passes through the region.
(a) A oscillates at half the frequency of B.
(b) A and B move in opposite directions.
(c) A and B must be separated by half of the wavelength.
(d) The displacements at A and B have equal magnitudes.
Choose the correct option:
A standing wave is produced on a string clamped at one end and free at the other. The length of the string ______.
The speed of sound in a medium depends on
A piano wire weighing 6⋅00 g and having a length of 90⋅0 cm emits a fundamental frequency corresponding to the "Middle C" \[\left( \nu = 261 \cdot 63 Hz \right)\]. Find the tension in the wire.
In Quincke's experiment the sound detected is changed from a maximum to a minimum when the sliding tube is moved through a distance of 2.50 cm. Find the frequency of sound if the speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
Two audio speakers are kept some distance apart and are driven by the same amplifier system. A person is sitting at a place 6.0 m from one of the speakers and 6.4 m from the other. If the sound signal is continuously varied from 500 Hz to 5000 Hz, what are the frequencies for which there is a destructive interference at the place of the listener? Speed of sound in air = 320 m s−1.
A cylindrical metal tube has a length of 50 cm and is open at both ends. Find the frequencies between 1000 Hz and 2000 Hz at which the air column in the tube can resonate. Speed of sound in air is 340 m s−1.
A piston is fitted in a cylindrical tube of small cross section with the other end of the tube open. The tube resonates with a tuning fork of frequency 512 Hz. The piston is gradually pulled out of the tube and it is found that a second resonance occurs when the piston is pulled out through a distance of 32.0 cm. Calculate the speed of sound in the air of the tube.
A U-tube having unequal arm-lengths has water in it. A tuning fork of frequency 440 Hz can set up the air in the shorter arm in its fundamental mode of vibration and the same tuning fork can set up the air in the longer arm in its first overtone vibration. Find the length of the air columns. Neglect any end effect and assume that the speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
A tuning fork of unknown frequency makes 5 beats per second with another tuning fork which can cause a closed organ pipe of length 40 cm to vibrate in its fundamental mode. The beat frequency decreases when the first tuning fork is slightly loaded with wax. Find its original frequency. The speed of sound in air is 320 m s−1.
A person riding a car moving at 72 km h−1 sound a whistle emitting a wave of frequency 1250 Hz. What frequency will be heard by another person standing on the road (a) in front of the car (b) behind the car? Speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1.
A violin player riding on a slow train plays a 440 Hz note. Another violin player standing near the track plays the same note. When the two are closed by and the train approaches the person on the ground, he hears 4.0 beats per second. The speed of sound in air = 340 m s−1. (a) Calculate the speed of the train. (b) What beat frequency is heard by the player in the train?
A car moving at 108 km h−1 finds another car in front it going in the same direction at 72 km h−1. The first car sounds a horn that has a dominant frequency of 800 Hz. What will be the apparent frequency heard by the driver in the front car? Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
An operator sitting in his base camp sends a sound signal of frequency 400 Hz. The signal is reflected back from a car moving towards him. The frequency of the reflected sound is found to be 410 Hz. Find the speed of the car. Speed of sound in air = 324 m s−1
A source emitting sound at frequency 4000 Hz, is moving along the Y-axis with a speed of 22 m s−1. A listener is situated on the ground at the position (660 m, 0). Find the frequency of the sound received by the listener at the instant the source crosses the origin. Speed of sound in air = 330 m s−1.
The speed of a transverse wave in an elastic string is v0. If the tension in the string is reduced to half, then the speed of the wave is given by:
Two tuning forks having frequencies 320 Hz and 340 Hz are sounded together to produce sound waves. The velocity of sound in air is 340 m/s. Find the difference in wavelength of these waves.
