Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
उत्तर
Given data:
l = 4m of R = 20Ω
In series with R’ = 2980Ω
E = 4 V
Since 20 is in series with 2980
Reff = 20 + 2980 = 3000
current I = `"V"/"R"_"eff" = 4/3000 = 1.3 xx 10^-3 "A"`
I = `1.3 xx 10^-3`A
Potential along the wire of 4 m length is,
`"V"/"l" - "IR"/"l" = (1.3 xx 10^-3 xx 20)/4`
`= (26 xx 10^-3)/4`
= 6.5 × 10-3 Vm-1
`"V"/"l" = 6.5 xx 10^-2 "Vm"^-1`
Potential = `0.65 xx 10^-2 "Vm"^-1`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Kirchhoff's rules for an electric network. Using Kirchhoff's rules, obtain the balance condition in terms of the resistances of four arms of Wheatstone bridge.
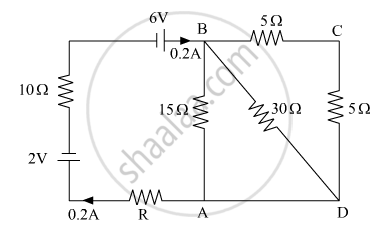
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points A and B?
A capacitor of capacitance 8.0 μF is connected to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a resistance of 24 Ω. Find the current in the circuit (a) just after the connections are made and (b) one time constant after the connections are made.
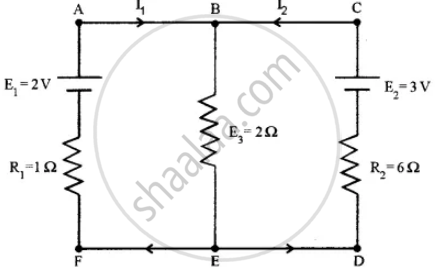
In the circuit shown in the figure below, E1 and E2 are two cells having emfs 2 V and 3 V respectively, and negligible internal resistance. Applying Kirchhoff’s laws of electrical networks, find the values of currents l1 and I2.
Twelve wires each having a resistance of 3 Ω are connected to form a cubical network. A battery of 10 V and negligible internal resistance is connected across the diagonally opposite corners of this network. Determine its equivalent resistance and the current along each edge of the cube.
State Kirchhoff’s current rule.
Assertion: Kirchhoff’s junction rule follows from conservation of charge.
Reason: Kirchhoff’s loop rule follows from conservation of momentum.
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `i_3/i_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is: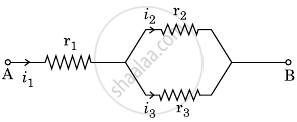
Kirchhoff’s junction rule is a reflection of ______.
- conservation of current density vector.
- conservation of charge.
- the fact that the momentum with which a charged particle approaches a junction is unchanged (as a vector) as the charged particle leaves the junction.
- the fact that there is no accumulation of charges at a junction.
