Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
उत्तर
Given:
Mass = m = 150 kg
Speed = v = 36 km/hr = 10 m/s
Radius of turn = r = 30 m
Let the horizontal force needed to make the turn be F. We have :
\[F = \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{r}} = \frac{150 \times (10 )^2}{30}\]
\[ = \frac{150 \times 100}{30} = 500 \text{ N}\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev/min in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N?
A disc revolves with a speed of `33 1/3` rev/min, and has a radius of 15 cm. Two coins are placed at 4 cm and 14 cm away from the centre of the record. If the co-efficient of friction between the coins and the record is 0.15, which of the coins will revolve with the record?
A coin placed on a rotating turntable just slips. If it is placed at a distance of 4 cm from the centre. If the angular velocity of the turntable is doubled, it will just slip at a distance of
A train A runs from east to west and another train B of the same mass runs from west to east at the same speed along the equator. A presses the track with a force F1 and B presses the track with a force F2.
An object follows a curved path. The following quantities may remain constant during the motion
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) magnitude of acceleration.
Find the acceleration of a particle placed on the surface of the earth at the equator due to earth's rotation. The diameter of earth = 12800 km and it takes 24 hours for the earth to complete one revolution about its axis.
Suppose the bob of the previous problem has a speed of 1.4 m/s when the string makes an angle of 0.20 radian with the vertical. Find the tension at this instant. You can use cos θ ≈ 1 − θ2/2 and SINθ ≈ θ for small θ.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. By what fraction is the balance reading less than his true weight?
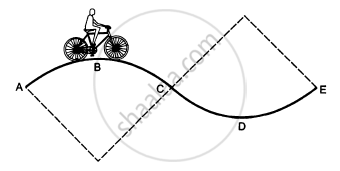
A track consists of two circular parts ABC and CDE of equal radius 100 m and joined smoothly as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing 100 kg together with the rider travels at a constant speed of 18 km/h on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take g = 10 m/s2.
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
A block of mass m moves on a horizontal circle against the wall of a cylindrical room of radius R. The floor of the room on which the block moves is smooth but the friction coefficient between the wall and the block is μ. The block is given an initial speed v0. As a function of the speed v writes
(a) the normal force by the wall on the block,
(b) the frictional force by a wall, and
(c) the tangential acceleration of the block.
(d) Integrate the tangential acceleration \[\left( \frac{dv}{dt} = v\frac{dv}{ds} \right)\] to obtain the speed of the block after one revolution.
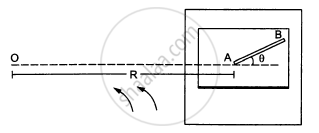
A table with smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω in a circular path of radius R (In the following figure). A smooth groove AB of length L(<<R) is made the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle θ with the radius OA of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point A in the groove and is released to move at the point A in the groove and is released to move along AB. Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point B.
A particle of mass 1 kg, tied to a 1.2 m long string is whirled to perform the vertical circular motion, under gravity. The minimum speed of a particle is 5 m/s. Consider the following statements.
P) Maximum speed must be `5sqrt5` m/s.
Q) Difference between maximum and minimum tensions along the string is 60 N.
Select the correct option.
The centripetal force of a body moving in a circular path, if speed is made half and radius is made four times the original value, will ____________.
A rigid body is rotating with angular velocity 'ω' about an axis of rotation. Let 'v' be the linear velocity of particle which is at perpendicular distance 'r' from the axis of rotation. Then the relation 'v = rω' implies that ______.
If a cyclist doubles his speed while negotiating a curve, how does the tendency to overturn vary?
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
