Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
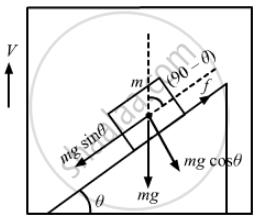
A small block of mass m is kept on a rough inclined surface of inclination θ fixed in an elevator. the elevator goes up with a uniform velocity v and the block does not slide on the wedge. The work done by the force of friction on the block in time t will be
विकल्प
zero
mgvt cos2θ
mgvt sin2θ
mgvt sin 2θ
उत्तर
mgvt sin2θ
Distance (d) travelled by the elevator in time t = vt
The block is not sliding on the wedge.
Then friction force (f) = mg sin \[\theta\] Work done by the friction force on the block in time t is given by
\[W = Fd\cos(90 - \theta)\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \text{ mg } \sin\theta \times d \times \cos(90 - \theta)\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \text{ mgd } \sin^2 \theta\]
\[ \therefore W = \text{ mgvt } \sin^2 \theta\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook?
When Neils Bohr shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
The sum of all electromagnetic forces between different particles of a system of charged particles is zero
At what distance should two charges, each equal to 1 C, be placed so that the force between them equals your weight ?
Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a separation of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude. Find the magnitude of the charge placed on either body.
Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20 N of Coulomb force on each other. What will be the force of the separation is increased to 25 cm?
No work is done by a force on an object if
(a) the force is always perpendicular to its velocity
(b) the force is always perpendicular to its acceleration
(c) the object is stationary but the point of application of the force moves on the object
(d) the object moves in such a way that the point of application of the force remains fixed.
A particle moves from a point \[\overrightarrow{r}_1 = \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] to another point
\[\overrightarrow{r}_2 = \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] acts on it. Find the work done by the force on the particle during the displacement.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Show that the work done by the applied force does not exceed 40 J.
A block of mass 2 kg kept at rest on an inclined plane of inclination 37° is pulled up the plane by applying a constant force of 20 N parallel to the incline. The force acts for one second. Find the kinetic energy of the block at the instant the force ceases to act. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A uniform chain of length L and mass M overhangs a horizontal table with its two third part on the table. The friction coefficient between the table and the chain is μ . Find the work done by friction during the period the chain slips off the table.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

The work done by an applied variable force, F = x + x3 from x = 0 m to x = 2m, where x is displacement, is:
A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by gravitational force?
A block of mass 1 kg is pushed up a surface inclined to horizontal at an angle of 30° by a force of 10 N parallel to the inclined surface (Figure). The coefficient of friction between block and the incline is 0.1. If the block is pushed up by 10 m along the incline, calulate
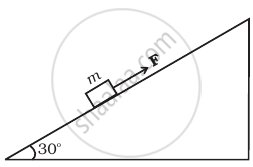
- work done against gravity
- work done against force of friction
- increase in potential energy
- increase in kinetic energy
- work done by applied force.
A block of mass m is taken from A to B slowly under the action of a constant force R Work done by this force is ______.

Work done by gas in cyclic process is ______ J.