Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small compass needle of magnetic moment ‘m’ is free to turn about an axis perpendicular to the direction of uniform magnetic field ‘B’. The moment of inertia of the needle about the axis is ‘I’. The needle is slightly disturbed from its stable position and then released. Prove that it executes simple harmonic motion. Hence deduce the expression for its time period.
उत्तर
The torque on the needle is τ = m × B
In magnitude τ = mB sinθ
Here τ is restoring torque and θ is the angle between m and B.
Therefore, in equilibrium `I (d^2θ)/dt^2 =-mBsinθ`
Negative sign with mB sinθ implies that restoring torque is in opposition to deflecting torque. For small values of θ in radians, we approximate sinθ= θ and get
`I (d^2θ)/dt^2 =-mBθ`
or
`(d^2θ)/dt^2 =-(mB)/Iθ`
This represents a simple harmonic motion. The square of the angular frequency is ω2 = mB/J and the time period is,`T = 2πsqrtI/(mB)`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
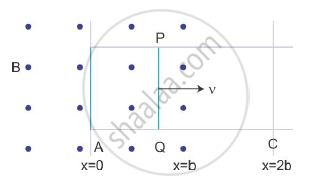
Sketch the change in flux, emf and force when a conducting rod PQ of resistance R and length l moves freely to and fro between A and C with speed v on a rectangular conductor placed in uniform magnetic field as shown in the figure
A short bar magnet of magnetic moment 0.9 J/T is placed with its axis at 30° to a uniform magnetic field. It experiences a torque of 0.063 J.
(i) Calculate the magnitude of the magnetic field.
(ii) In which orientation will the bar magnet be in stable equilibrium in the magnetic field?
Can a charged particle be accelerated by a magnetic field? Can its speed be increased?
A particle moves in a region with a uniform magnetic field and a parallel, uniform electric field. At some instant, the velocity of the particle is perpendicular to the field direction. The path of the particle will be
You are facing a circular wire carrying an electric current. The current is clockwise as seen by you. Is the field at the centre coming towards you or going away from you?
A long wire carrying a current i is bent to form a place along α . Find the magnetic field B at a point on the bisector of this angle situated at a distance x from the vertex.
Figure shows a part of an electric circuit. The wires AB, CD and EF are long and have identical resistance. The separation between the neighbouring wires is 1.0 cm. The wires AE and BF have negligible resistance and the ammeter reads 30 A. Calculate the magnetic force per unit length of AB and CD.

A straight horizontal conducting rod of length 0.45 m and mass 60 g is suspended by two vertical wires at its ends. A current of 5.0 A is set up in the rod through the wires.
(a) What magnetic field should be set up normal to the conductor in order that the tension in the wires is zero?
(b) What will be the total tension in the wires if the direction of current is reversed keeping the magnetic field same as before?
(Ignore the mass of the wires) g = 9.8 m s–2.
A charged particle is moving on circular path with velocity v in a uniform magnetic field B, if the velocity of the charged particle is doubled and strength of magnetic field is halved, then radius becomes ______.
A current of 3 A is flowing in a linear conductor having a length of 40 cm. The conductor is placed in a magnetic field of strength of 500 gauss and makes an angle of 30° with the direction of the field. It experiences a force of magnitude:
