Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 80 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the candle flame at a distance of 20 cm from its pole.
- Which type of mirror should the student use?
- Find the magnification of the image produced.
- Find the distance between the object and its image.
- Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case and mark the distance between the object and its image.
उत्तर
(a) A real image can be projected on a screen using a concave mirror. In the given case, the student should use a concave mirror.
(b) \[\text{ Magnification }\left( m \right)\text{ is given by }\]
\[m = - \frac{v}{u}\]
Here,
\[u = \text{ Distance of the object }\]
\[v =\text{ Distance of the image }\]
\[ \therefore m = \frac{- \left( - 80 \right)}{\left( - 20 \right)} = - 4\]
(c)
The object and the image are on the same side of the mirror.
Distance of the object from the lens = 20 cm
Distance of the image from the lens = 80 cm
Thus,
Distance between the object and the image = 80 − 20 = 60 cm
(d)
To draw a ray diagram, we need to find the focal length of the mirror.
According to the mirror formula,
\[\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{u} + \frac{1}{v}\]
Here,
u = Distance of the object
v = Distance of the image
f = Focal length of the mirror
Now,
\[\frac{1}{f} = \frac{1}{- 20} + \frac{1}{- 80}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{f} = - \left( \frac{4 + 1}{80} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{1}{f} = - \left( \frac{5}{80} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow f = - \left( \frac{80}{5} \right) = - 16 cm\]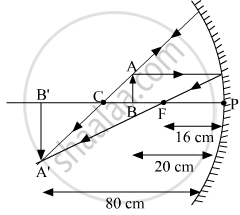
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the difference between a real image and a virtual image? Give one example of each type of image
A concave mirror produces magnification of +4. The object is placed:
(a) at the focus
(b) between focus and centre of curvature
(c) between focus and pole
(d) between the centre of curvature
Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of a virtual magnified image of an object by a convex lens. In your diagram, the position of object and image with respect to the principal focus should be shown clearly.
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens is used as a magnifying glass to observe a small object. Mark on your diagram the foci of the lens and the position of the eye.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance 30 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 60 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.4 cm, find the height of its image.
The image of a candle flame placed at a distance 36 cm from a spherical lens is formed on a screen placed at a distance of 72 cm from the lens. Identify the type of lens and calculate its focal length. If the height of the flame is 2.5 cm, find the height of its image.
At which position will you keep an object in front of a convex lens so as to get a real image of the same size as the object? Draw a figure.
The lens of the eye is flattened when looking at nearby objects.
The image of a candle flame formed by a lens is obtained on a screen placed on the other side of the lens. If the image is three times the size of the flame and the distance between lens and image is 80 cm, at what distance should the candle be placed from the lens? What is the nature of the image at a distance of 80 cm and the lens?
Ravi kept a book at a distance of 10 cm from the eyes of his friend Hari. Hari is not able to read anything written in the book. Give reasons for this?
