Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A system goes from P to Q by two different paths in the P-V diagram as shown in figure. Heat given to the system in path 1 is 1000 J. The work done by the system along path 1 is more than path 2 by 100 J. What is the heat exchanged by the system in path 2?
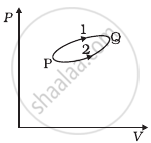
उत्तर
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
∆Q = AU + ∆W.
Let us apply this for each path.
For path 1: Heat given Q1 = + 1000 J
Let work done for path 1 = W1
For path 2: Work done (W2) = (W1 – 100) J
Heat has given Q2 = ?
A change in internal energy between two states for the different paths is the same.
∴ ∆U = Q1 – W1 = Q2 – W2
1000 – W1 = Q2 – (W1 – 100)
⇒ Q2 = 1000 – 100 = 900 J
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Refer to figure. Let ∆U1 and ∆U2 be the change in internal energy in processes A and B respectively, ∆Q be the net heat given to the system in process A + B and ∆W be the net work done by the system in the process A + B.

(a) ∆U1 + ∆U2 = 0
(b) ∆U1 − ∆U2 = 0
(c) ∆Q − ∆W = 0
(d) ∆Q + ∆W = 0
Calculate the heat absorbed by a system in going through the cyclic process shown in figure.
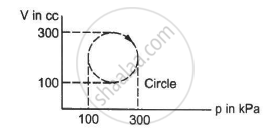
A sample of gas absorbs 4000 kJ of heat and surrounding does 2000 J of work on sample. What is the value of ∆U?
When heat energy of 2000 joules is supplied to a gas at constant pressure 2.1 x 105 N/m2, there is an increase in its volume equal to 2.5 x 10-3 m3. The increase in internal energy of the gas in joules is ____________.
In a given process for an ideal gas, dW = 0 and dQ < 0. Then for the gas ____________.
A cycle followed by an engine (made of one mole of perfect gas in a cylinder with a piston) is shown in figure.
A to B : volume constant
B to C : adiabatic
C to D : volume constant
D to A : adiabatic
VC = VD = 2VA = 2VB
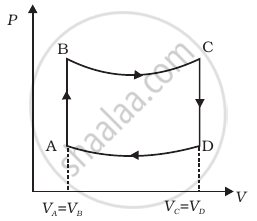
- In which part of the cycle heat is supplied to the engine from outside?
- In which part of the cycle heat is being given to the surrounding by the engine?
- What is the work done by the engine in one cycle? Write your answer in term of PA, PB, VA.
- What is the efficiency of the engine?
(γ = `5/3` for the gas), (Cv = `3/2` R for one mole)
If the adiabatic ratio for a gas is 5/3, find the molar specific heat capacity of the gas at (i) constant volume (ii) constant pressure.
In an adiabatic process, W = ______.
For an isothermal and reversible expansion of 0.5 mol of an ideal gas Wmax is - 3.918 kJ. The value of ΔU is ______.
Calculate work done when 2 moles of ideal gas expands by 5 dm3 isothermally at pressure 1.2 bar.
