Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
AB and CD are two intersecting lines. Find a point equidistant from AB and CD, and also at a distance of 1.8 cm from another given line EF.
उत्तर
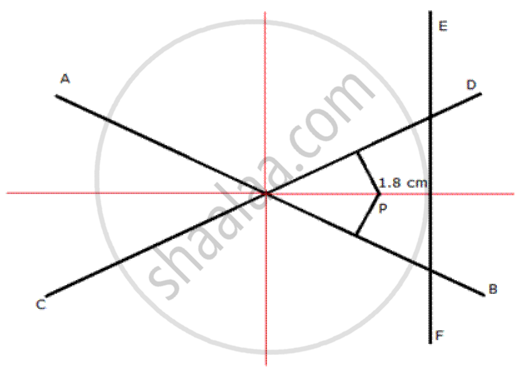
Draw angle bisector of AB and CD . Draw perpendio..ilars from AB and CD on angle bisector, say P. Pis the required point which is equidistant from AB and CD and at a distAnce of 1.8 cm from FF.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Describe the locus of a point in space, which is always at a distance of 4 cm from a fixed point.
Plot the points A(2, 9), B(–1, 3) and C(6, 3) on graph paper. On the same graph paper draw the locus of point A so that the area of ΔABC remains the same as A moves.
Construct a rhombus ABCD with sides of length 5 cm and diagonal AC of length 6 cm. Measure ∠ ABC. Find the point R on AD such that RB = RC. Measure the length of AR.
Construct a Δ XYZ in which XY= 4 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ∠ Y = 1200. Locate a point T such that ∠ YXT is a right angle and Tis equidistant from Y and Z. Measure TZ.
A and B are fixed points while Pis a moving point, moving in a way that it is always equidistant from A and B. What is the locus of the path traced out by the pcint P?
Draw and describe the lorus in the following cases:
The locus of points at a distance of 4 cm from a fixed line.
Describe completely the locus of points in the following cases:
Centre of a circle of varying radius and touching the two arms of ∠ ABC.
Using only ruler and compasses, construct a triangle ABC 1 with AB = 5 cm, BC = 3.5 cm and AC= 4 cm. Mark a point P, which is equidistant from AB, BC and also from Band C. Measure the length of PB.
Construct a triangle BPC given BC = 5 cm, BP = 4 cm and .
i) complete the rectangle ABCD such that:
a) P is equidistant from AB and BCV
b) P is equidistant from C and D.
ii) Measure and record the length of AB.
Without using set squares or protractor construct a triangle ABC in which AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm and ∠ABC = 120°.
(i) Locate the point P such that ∠BAp = 90° and BP = CP.
(ii) Measure the length of BP.
