Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following diagrams (Fig. 5) show the use of a vernier caliper under three different situations. Study the diagrams carefully and note down the vernier readings in each case.
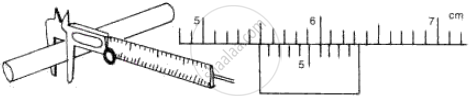
(a) Measuring the diameter of the rod
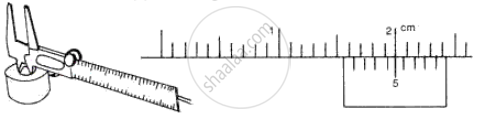
(b) Measuring Internal diameter of a cavity

(c) Measuring depth of a cavity
उत्तर

(a) Measuring the diameter of the rod

(b) Measuring Internal diameter of a cavity

(c) Measuring the depth of a cavity
Least count of vernier caliper = 0.01 cm
(i) Main scale reading = 5.5 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 6 Vernier scale reading = 6 × 0.01 cm = 0.06 cm
Diameter of rod = 5.5 + 0.06 = 5.56 cm
(ii) Main scale reading = 1.6 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 5
Vernier scale reading = 5 × 0.01 cm = 0.05 cm
Internal diameter of a cavity = 1.6 + 0.05 = 1.65 cm
(iii) Main scale reading = 3.1 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 5 Vernier scale reading = 5 × 0.01 cm = 0.05 cm
Depth of a cavity = 3.1 + 0.05 = 3.15 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When is a vernier Callipers said to be free from zero error?
Name the part of the vernier callipers which is used to measure the following
Internal diameter of a mug
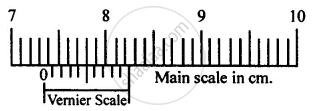
In figure for vernier callipers, calculate the length recorded.
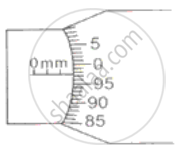
What do you understand by the following term as applied to screw gauge?
Zero error
In the following figure, the pitch of the screw is 1 mm. Calculate:
(i) the least count of screw gauge and
(ii) the reading represented in the figure.
Name the measuring employed to measure the diameter of a pencil.
How will you measure the least count of vernier caliper?
The precision of vernier calipers is ______ mm.
