Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The following diagrams (Fig. 5) show the use of a vernier caliper under three different situations. Study the diagrams carefully and note down the vernier readings in each case.
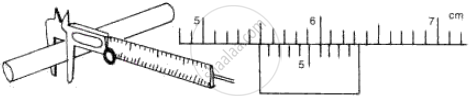
(a) Measuring the diameter of the rod
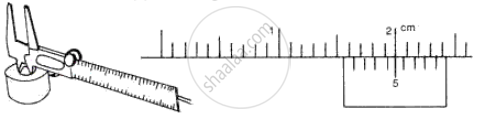
(b) Measuring Internal diameter of a cavity

(c) Measuring depth of a cavity
उत्तर

(a) Measuring the diameter of the rod

(b) Measuring Internal diameter of a cavity

(c) Measuring the depth of a cavity
Least count of vernier caliper = 0.01 cm
(i) Main scale reading = 5.5 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 6 Vernier scale reading = 6 × 0.01 cm = 0.06 cm
Diameter of rod = 5.5 + 0.06 = 5.56 cm
(ii) Main scale reading = 1.6 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 5
Vernier scale reading = 5 × 0.01 cm = 0.05 cm
Internal diameter of a cavity = 1.6 + 0.05 = 1.65 cm
(iii) Main scale reading = 3.1 cm
Vernier scale division coinciding with main scale = 5 Vernier scale reading = 5 × 0.01 cm = 0.05 cm
Depth of a cavity = 3.1 + 0.05 = 3.15 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The thimble of a screw gauge has 50 divisions. The spindle advances 1 mm when the screw is turned through two revolutions.
(i) What is the pitch of the screw gauge?
(ii) What is the least count of the screw gauge?
Define metre according to the old definition.
Why is the metre length in terms of the wavelength of light considered more accurate?
Up to how many decimal places can a common vernier callipers measure the length in cm?
What is the least count in the case of the following instrument?
Spring balance
Consider the following case where the zero of vernier scale and the zero of the main scale are clearly seen. If L.C. of the vernier calipers is 0.01 cm, write the zero error and zero correction of the following.
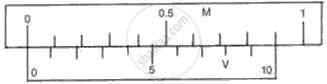
Least count of a vernier caliper is ______ cm.
