Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Give two reasons.
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why?
उत्तर १
On losing a proton, carboxylic acids form carboxylate ion and phenol forms phenoxide ion as follows:

Now, the negative charge is delocalized in both molecules as follows:
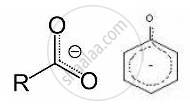
The conjugate base of carboxylic acid has two resonance structures in which the negative charge is delocalized over two oxygen atoms (since O is more electronegative than C), stabilising the carboxylate ion.
On the other hand, in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalized over the entire molecule on the less electronegative atom (carbon). Thus, the resonance of phenoxide is not important in comparison to resonance in carboxylate ion.
Further, in carboxylate ion the negative charge is effectively delocalized over two oxygen atoms, whereas it is less effectively delocalized over one oxygen atom and less electronegative carbon atom.
Thus, phenol is less acidic than carboxylic acids. In other words, carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenol.
उत्तर २
Resonance structures of phenoxide ion are:
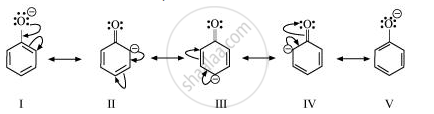
It can be observed from the resonance structures of phenoxide ion that in II, III and IV, less electronegative carbon atoms carry a negative charge. Therefore, these three structures contribute negligibly towards the resonance stability of the phenoxide ion. Hence, these structures can be eliminated. Only structures I and V carry a negative charge on the more electronegative oxygen atom.
Resonance structures of carboxylate ion are:

In the case of carboxylate ion, resonating structures I′ and II′ contain a charge carried by a more electronegative oxygen atom.
Further, in resonating structures I′ and II′, the negative charge is delocalized over two oxygen atoms. But in resonating structures I and V of the phexoxide ion, the negative charge is localized on the same oxygen atom. Therefore, the resonating structures of carboxylate ion contribute more towards its stability than those of phenoxide ion. As a result, carboxylate ion is more resonance-stabilized than phenoxide ion. Hence, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol.
Notes
Students can refer to the provided solutions based on their preferred marks.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why pKa of F-CH2-COOH is lower than that of Cl−CH2−COOH?
Distinguish between the following : Benzoic acid and methyl benzoate
Which acid of the pair shown here would you expect to be stronger?
CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br)CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2CH2COOH (acid strength)
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
Benzoic acid, 4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3, 4-Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
Write the reactions involved Hell-Volhard Zelinsky reaction?
What happens when Salicylic acid is treated with (CH3CO)2 O/H+?
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated:
F - CH2COOH, O2N - CH2 COOH CH3 COOH,HCOOH - acid character.
Assertion: Formaldehyde is a planar molecule.
Reason: It contains sp2 hybridised carbon atom.
Acidity of BF3 can be explained on the basis of which of the following concepts?
A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with 50% NaOH solution gives
When propionamide reacts with Br2 in the presence of alkali the product is ______.
Na2CO3 cannot be used in place of (NH4)2CO3 for the precipitation of the V group because ______.
Formic acid and formaldehyde can be distinguished by treating with ______.
Describe the action of alcoholic potassium hydroxide (alc. KOH) on isopropyl bromide.
