Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An ac generator generates an emf which is given by e = 311 sin (240 πt) V. Calculate:
- frequency of the emf.
- r.m.s. value of the emf.
उत्तर
(1) Given that
e = 311 sin (240 πt) V ...(i)
∵ e = e0 sin (ωt) V ...(ii)
From equations (i) and (ii)
e0 = 311 and ωt = 240 πt
∴ ω = 240 π
f = `omega/(2pi)`
`= (240 pi)/(2pi)`
= 120 cycle/s
e0 = Peak emf of the generator = 33
∵ Peak emf = rms · emf × `sqrt2`
∴ rms = `1/sqrt2` peak emf
= 0.707 × 311 = 219.87 volts
∴ rms = 219.87 volts
(2) Given the number of turns in the primary winding is NP = 60 turns.
The number of turns in secondary winding is NS = 3000 turns.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Six lead-acid types of secondary cells each of emf 2.0 V and internal resistance 0.015 Ω are joined in series to provide a supply to a resistance of 8.5 Ω. What are the current drawn from the supply and its terminal voltage?
A resistor R is connected to a cell of-emf e and internal resistance r. The potential difference across the resistor R is found to be V. State the relation between e, V, Rand r.
A potentiometer wire of length 1.0 m has a resistance of 15 Ω. It is connected to a 5 V battery in series with a resistance of 5 Ω. Determine the emf of the primary cell which gives a balance point at 60 cm.
How many time constants will elapse before the power delivered by a battery drops to half of its maximum value in an RC circuit?
A plate of area 10 cm2 is to be electroplated with copper (density 9000 kg m−3) to a thickness of 10 micrometres on both sides, using a cell of 12 V. Calculate the energy spent by the cell in the process of deposition. If this energy is used to heat 100 g of water, calculate the rise in the temperature of the water. ECE of copper = 3 × 10−7 kg C−1and specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1.
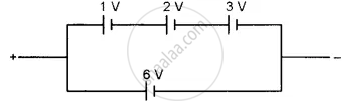
Find the emf of the battery shown in the figure:
A conductor of length 'l' is rotated about one of its ends at a constant angular speed 'ω' in a plane perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field B. Plot graphs to show variations of the emf induced across the ends of the conductor with (i) angular speed ω and (ii) length of the conductor l.
