Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
An ideal gas is taken in a cyclic process as shown in the figure. Calculate
- work done by the gas
- work done on the gas
- Net work done in the process

उत्तर
a. Work done by the gas (along with AB)
W = P × ΔV = 600 × 3 = 1800 J
W = 1.8 kJ
b. Work is done on the gas (along with BC)
W = −P × ΔV = −400 × 3 = −1200 J
W = −1.2 kJ
c. Net work done in the process = Area under the curve AB
= Rectangle area + triangle area
= `("l" xx "b") + (1/2 xx "b" xx "h")`
= `(400 xx 3) + (1/2 xx 3 xx 200)`
= 1200 + 300
= 1500 J
W = 1.5 kJ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a p-V diagram showing negative work with varying pressure.
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Write a note on free expansion.
When a cycle tyre suddenly bursts, the air inside the tyre expands. This process is ____________.
What is a cyclic process?
In a petrol engine, (internal combustion engine) air at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 20°C is compressed in the cylinder by the piston to `1/8` of its original volume. Calculate the temperature of the compressed air. (For air γ = 1.4)
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

Which of the following processes is reversible?
Consider P-V diagram for an ideal gas shown in figure.
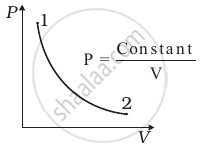
Out of the following diagrams (figure), which represents the T-P diagram?
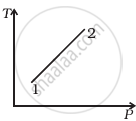 (i) |
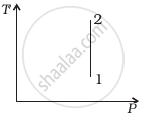 (ii) |
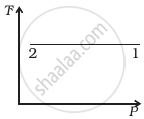 (iii) |
 (iv) |
In a cyclic process, if ΔU = internal energy, W = work done, Q = Heat supplied then ______.
