Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
उत्तर
During a collision, when balls are in contact, the kinetic energy of the balls is transformed into potential energy. The kinetic energy remains the same before and after the collision. Therefore, in the described elastic collision, the total kinetic energy is not conserved.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
Define the following:
Coefficient of restitution
A ball of mass 0.1 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with a ball of unknown mass, initially at rest. If the 0 .1 kg ball rebounds at one-third of its original speed, the mass of the other ball is ______.
A particle of mass 'm' collides with another stationary particle of mass 'M'. A particle of mass 'm' stops just after collision. The coefficient of restitution is ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. There are four regions A, B, C and D in which the relation between potential energy V, kinetic energy (K) and total energy E is as given below:
Region A : V > E
Region B : V < E
Region C : K > E
Region D : V > K
State with reason in each case whether a particle can be found in the given region or not.
The bob A of a pendulum released from horizontal to the vertical hits another bob B of the same mass at rest on a table as shown in figure.
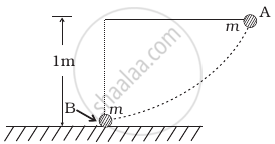
If the length of the pendulum is 1 m, calculate
- the height to which bob A will rise after collision.
- the speed with which bob B starts moving. Neglect the size of the bobs and assume the collision to be elastic.
An alpha-particle of mass m suffers 1-dimensional elastic collision with a nucleus at rest of unknown mass. It is scattered directly backwards losing, 64% of its initial kinetic energy. The mass of the nucleus is ______.
