Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e. when they are in contact)?
Solution
During a collision, when balls are in contact, the kinetic energy of the balls is transformed into potential energy. The kinetic energy remains the same before and after the collision. Therefore, in the described elastic collision, the total kinetic energy is not conserved.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
Define coefficient of restitution.
Solve the following problem.
A marble of mass 2m travelling at 6 cm/s is directly followed by another marble of mass m with double speed. After a collision, the heavier one travels with the average initial speed of the two. Calculate the coefficient of restitution.
A block of mass 'm' moving along a straight line with constant velocity `3vec"v"` collides with another block of same mass at rest. They stick together and move with common velocity. The common velocity is ______.
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
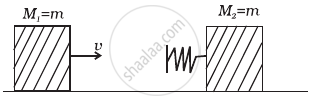
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
In an elastic collision of two billiard balls, which of the following quantities remain conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact).
- Kinetic energy.
- Total linear momentum?
Give reason for your answer in each case.
Consider a one-dimensional motion of a particle with total energy E. There are four regions A, B, C and D in which the relation between potential energy V, kinetic energy (K) and total energy E is as given below:
Region A : V > E
Region B : V < E
Region C : K > E
Region D : V > K
State with reason in each case whether a particle can be found in the given region or not.
A particle of mass m with an initial velocity u`hat"i"` collides perfectly elastically with a mass 3m at rest. It moves with a velocity v`hat"j"` after collision, then, v is given by :
A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and required 1 s to cover. How long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start?
