Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
Solution
No, in an inelastic collision, kinetic energy is always lost, meaning the total kinetic energy of the billiard balls before the collision will always be greater than after the collision.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
Answer carefully, with reason:
If the potential energy of two billiard balls depends only on the separation distance between their centres, is the collision elastic or inelastic? (Note, we are talking here of potential energy corresponding to the force during collision, not gravitational potential energy.)
A trolley of mass 200 kg moves with a uniform speed of 36 km/h on a frictionless track. A child of mass 20 kg runs on the trolley from one end to the other (10 m away) with a speed of 4 m s–1 relative to the trolley in a direction opposite to the its motion, and jumps out of the trolley. What is the final speed of the trolley? How much has the trolley moved from the time the child begins to run?
Define the following:
Coefficient of restitution
Two different unknown masses A and B collide. A is initially at rest when B has a speed v. After collision B has a speed v/2 and moves at right angles to its original direction of motion. Find the direction in which A moves after the collision.
A bomb of mass 9 kg explodes into two pieces of mass 3 kg and 6 kg. The velocity of mass 3 kg is 16 m/s, The kinetic energy of mass 6 kg is ____________.
A mass M moving with velocity 'v' along x-axis collides and sticks to another mass 2M which is moving along Y-axis with velocity 3v. After collision, the velocity of the combination is ______.
A particle of mass 'm' collides with another stationary particle of mass 'M'. A particle of mass 'm' stops just after collision. The coefficient of restitution is ______.
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V as shown in figure.
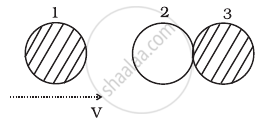
If the collision is elastic, which of the following (Figure) is a possible result after collision?
A particle of mass m with an initial velocity u`hat"i"` collides perfectly elastically with a mass 3m at rest. It moves with a velocity v`hat"j"` after collision, then, v is given by :
