Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Answer carefully, with reason:
If the potential energy of two billiard balls depends only on the separation distance between their centres, is the collision elastic or inelastic? (Note, we are talking here of potential energy corresponding to the force during collision, not gravitational potential energy.)
Solution
The potential energy depends on the separation distance between centres; this means that during the collision, the force acting between the bodies is conservative; therefore, energy will be conserved. Thus, the collision will be elastic.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?

Which of the following potential energy curves in Fig. cannot possibly describe the elastic collision of two billiard balls? Here r is distance between centres of the balls.

Consider the decay of a free neutron at rest : n → p + e–
Show that the two-body decay of this type must necessarily give an electron of fixed energy and, therefore, cannot account for the observed continuous energy distribution in the β-decay of a neutron or a nucleus

Solve the following problem.
A spring ball of mass 0.5 kg is dropped from some height. On falling freely for 10 s, it explodes into two fragments of mass ratio 1:2. The lighter fragment continues to travel downwards with a speed of 60 m/s. Calculate the kinetic energy supplied during the explosion.
A ball is thrown vertically down from height of 80 m from the ground with an initial velocity 'v'. The ball hits the ground, loses `1/6`th of its total mechanical energy, and rebounds back to the same height. If the acceleration due to gravity is 10 ms-2, the value of 'v' is
In Rutherford experiment, for head-on collision of a-particles with a gold nucleus, the impact parameter is ______.
A body of mas 'm' moving with speed 3 m/s collides with a body of mass '2m' at rest. The coalesced mass will start to move with a speed of ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
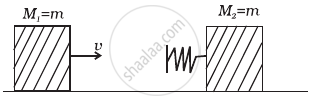
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
A ball falls from a height of 1 m on a ground and it loses half its kinetic energy when it hits the ground. What would be the total distance covered by the ball after sufficiently long time?
