Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the ______ on the system.
विकल्प
External force
Sum of the internal forces
उत्तर
The rate of change of total momentum of a many-particle system is proportional to the external force on the system.
Explanation:
Internal forces, regardless of their direction, are incapable of altering the total momentum of a body. Hence, the rate of change in total momentum of many particle systems is proportional to the external force on the system.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer carefully, with reason:
In an inelastic collision of two billiard balls, is the total kinetic energy conserved during the short time of collision of the balls (i.e., when they are in contact)?
Two identical ball bearings in contact with each other and resting on a frictionless table are hit head-on by another ball bearing of the same mass moving initially with a speed V. If the collision is elastic, which of the following figure is a possible result after collision?

A particle of mass 'm' collides with another stationary particle of mass 'M'. A particle of mass 'm' stops just after collision. The coefficient of restitution is ______.
A block of mass 'm' moving along a straight line with constant velocity `3vec"v"` collides with another block of same mass at rest. They stick together and move with common velocity. The common velocity is ______.
A bullet fired from gun with a velocity 30 m/s at an angle of 60° with horizontal direction. At the highest point of its path, the bullet explodes into two parts with masses in the ratio 1:3. The lighter mass comes to rest immediately. Then the speed of the heavier mass is
Two blocks M1 and M2 having equal mass are free to move on a horizontal frictionless surface. M2 is attached to a massless spring as shown in figure. Iniially M2 is at rest and M1 is moving toward M2 with speed v and collides head-on with M2.
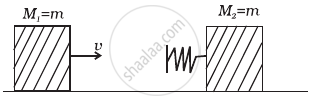
- While spring is fully compressed all the KE of M1 is stored as PE of spring.
- While spring is fully compressed the system momentum is not conserved, though final momentum is equal to initial momentum.
- If spring is massless, the final state of the M1 is state of rest.
- If the surface on which blocks are moving has friction, then collision cannot be elastic.
A ball of mass m, moving with a speed 2v0, collides inelastically (e > 0) with an identical ball at rest. Show that for a general collision, the angle between the two velocities of scattered balls is less than 90°.
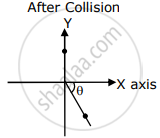
A ball of mass 10 kg moving with a velocity of 10`sqrt3` ms–1 along the X-axis, hits another ball of mass 20 kg which is at rest. After collision, the first ball comes to rest and the second one disintegrates into two equal pieces. One of the pieces starts moving along Y-axis at a speed of 10 m/s. The second piece starts moving at a speed of 20 m/s at an angle θ (degree) with respect to the X-axis.
The configuration of pieces after the collision is shown in the figure.
The value of θ to the nearest integer is ______.
A drunkard walking in a narrow lane takes 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, followed again by 5 steps forward and 3 steps backward, and so on. Each step is 1 m long and required 1 s to cover. How long the drunkard takes to fall in a pit 13 m away from the start?
An alpha-particle of mass m suffers 1-dimensional elastic collision with a nucleus at rest of unknown mass. It is scattered directly backwards losing, 64% of its initial kinetic energy. The mass of the nucleus is ______.
