Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 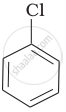 |
| (b) | 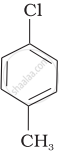 |
| (c) | 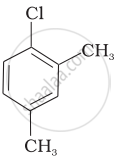 |
विकल्प
(a) < (b) < (c)
(b) < (a) < (c)
(c) < (b) < (a)
(a) < (c) < (b)
उत्तर
(c) < (b) < (a)
Explanation:
The presence of electron releasing group at ortho- and para-positions decreases the reactivity of haloarenes. Because of the possible repulsion, it is less likely for the electron-rich nucleophile to approach electron-rich arenes. The more the electron-releasing group is attached lesser, will be the rate of reaction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when \[\ce{CH3 - Br}\] is treated with KCN?
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
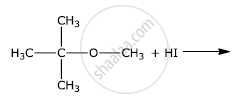
The presence of nitro group (−NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
What is Grignard reagent?
Write chemical equation in support of your answer.
Out of 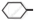 Cl and
Cl and 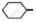 CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
CH2- Cl, which one is more reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction and why?
Out of (CH3)3 C-Br and (CH3)3 C-I, which one is more reactive towards SN1 and why?
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 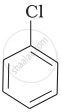 |
| (b) | 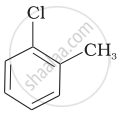 |
| (c) | 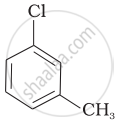 |
Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain.
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
Why haloarenes are not reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? Give two reactions.
