Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 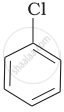 |
| (b) | 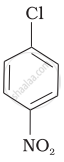 |
| (c) | 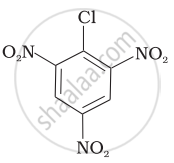 |
विकल्प
(c) < (b) < (a)
(b) < (c) < (a)
(a) < (c) < (b)
(a) < (b) < (c)
उत्तर
(a) < (b) < (c)
Explanation:
The presence of an electron-withdrawing group (–NO2) at ortho- and para-positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes. The presence of a nitro group at ortho- and para-positions withdraws the electron density from the benzene ring and thus facilitates the attack of the nucleophile on haloarene. The carbanion thus formed is stabilised through resonance. The negative charge appeared at ortho- and para-positions with respect to the halogen substituent is stabilised by the –NO2 group.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What happens when \[\ce{CH3 - Br}\] is treated with KCN?
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
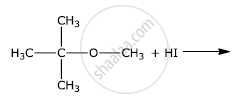
The presence of nitro group (−NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Write the product formed on reaction of D-glucose with Br2 water.
Out of (CH3)3 C-Br and (CH3)3 C-I, which one is more reactive towards SN1 and why?
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 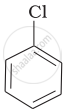 |
| (b) | 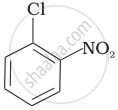 |
| (c) | 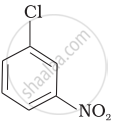 |
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 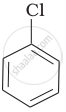 |
| (b) | 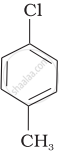 |
| (c) | 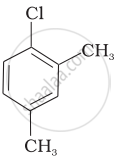 |
Allyl chloride is hydrolysed more readily than n-propyl chloride. Why?
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
Why haloarenes are not reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? Give two reactions.
