Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Assertion (A): For the radiation of a frequency greater than the threshold frequency, the photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation.
- Reason (R): Greater the number of energy quanta available, the greater the number of electrons absorbing the energy quanta and the greater the number of electrons coming out of the metal.
विकल्प
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
If both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
If Assertion is true but Reason is false.
If both Assertion and Reason are false.
उत्तर
If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Explanation:
When the frequency of the incident radiation exceeds the threshold frequency, the photoelectric current is proportional to the intensity of the radiation. As a result, the assertion is correct. As the intensity rises, so does the number of energy quanta accessible. By absorbing more energy quanta, a bigger number of electrons are emitted. A higher number of electrons equals a higher current. As a result, the photoelectric current becomes proportional to radiation intensity. So, the reason is also true, and it adequately explains the assumption.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Monochromatic radiation of wavelength 640.2 nm (1 nm = 10−9 m) from a neon lamp irradiates photosensitive material made of caesium on tungsten. The stopping voltage is measured to be 0.54 V. The source is replaced by an iron source and its 427.2 nm line irradiates the same photo-cell. Predict the new stopping voltage.
Every metal has a definite work function. Why do all photoelectrons not come out with the same energy if incident radiation is monochromatic? Why is there an energy distribution of photoelectrons?
Can we find the mass of a photon by the definition p = mv?
It is found that yellow light does not eject photoelectrons from a metal. Is it advisable to try with orange light or with green light?
In which of the following situations, the heavier of the two particles has smaller de Broglie wavelength? The two particles
(a) move with the same speed
(b) move with the same linear momentum
(c) move with the same kinetic energy
(d) have fallen through the same height
Show that it is not possible for a photon to be completely absorbed by a free electron.
The electric field associated with a light wave is given by `E = E_0 sin [(1.57 xx 10^7 "m"^-1)(x - ct)]`. Find the stopping potential when this light is used in an experiment on photoelectric effect with the emitter having work function 1.9 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
The work function for a metal surface is 4.14 eV. The threshold wavelength for this metal surface is ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions.
| The figure shows the variation of photoelectric current measured in a photocell circuit as a function of the potential difference between the plates of the photocell when light beams A, B, C and D of different wavelengths are incident on the photocell. Examine the given figure and answer the following questions: |
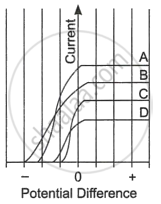
- Which light beam has the highest frequency and why?
- Which light beam has the longest wavelength and why?
- Which light beam ejects photoelectrons with maximum momentum and why?
