Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a 20 W bulb emitting light of wavelength 5000 Å and shining on a metal surface kept at a distance 2 m. Assume that the metal surface has work function of 2 eV and that each atom on the metal surface can be treated as a circular disk of radius 1.5 Å.
- Estimate no. of photons emitted by the bulb per second. [Assume no other losses]
- Will there be photoelectric emission?
- How much time would be required by the atomic disk to receive energy equal to work function (2 eV)?
- How many photons would atomic disk receive within time duration calculated in (iii) above?
- Can you explain how photoelectric effect was observed instantaneously?
उत्तर
According to the problem, P = 20 W, λ = 5000 Å = 5000 × 10–10 m, distance (d) = 2 m, work function
Now, Number of photon emitted by bulb per second, n' =
i. Number of photon emitted by bulb per second is n’ =
=
⇒ n' = 5 × 1019/sec
ii. Energy of the incident photon =
=
= 2.48 ev
As this energy is greater than 2 eV (i.e., a work function of the metal surface), hence photoelectric emission takes place.
iii. Let Δt be the time spent in getting the energy

Consider the figure, if P is the power of source then energy received by the atomic disc
⇒ Δt =
=
= 2.84 s
iv. Number of photons received by the atomic disc in time Δt is
N =
=
=
= 2
Now let us discuss the last part in detail. As the time of emission of electrons is 11.04 s.
v. In photoelectric emission, there is a collision between the incident photon and free electron of the metal surface, which lasts for a very short interval of time (≈ 10–9 s), hence we say photoelectric emission is instantaneous.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Light of intensity 10−5 W m−2 falls on a sodium photo-cell of surface area 2 cm2. Assuming that the top 5 layers of sodium absorb the incident energy, estimate time required for photoelectric emission in the wave-picture of radiation. The work function for the metal is given to be about 2 eV. What is the implication of your answer?
What is the speed of a photon with respect to another photon if (a) the two photons are going in the same direction and (b) they are going in opposite directions?
The work function of a metal is hv0. Light of frequency v falls on this metal. Photoelectric effect will take place only if
When stopping potential is applied in an experiment on photoelectric effect, no photoelectric is observed. This means that
A point source of light is used in a photoelectric effect. If the source is removed farther from the emitting metal, the stopping potential
A point source causes photoelectric effect from a small metal plate. Which of the following curves may represent the saturation photocurrent as a function of the distance between the source and the metal?

A totally reflecting, small plane mirror placed horizontally faces a parallel beam of light, as shown in the figure. The mass of the mirror is 20 g. Assume that there is no absorption in the lens and that 30% of the light emitted by the source goes through the lens. Find the power of the source needed to support the weight of the mirror.
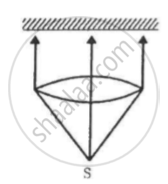
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
Find the maximum magnitude of the linear momentum of a photoelectron emitted when a wavelength of 400 nm falls on a metal with work function 2.5 eV.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
When a metal plate is exposed to a monochromatic beam of light of wavelength 400 nm, a negative potential of 1.1 V is needed to stop the photo current. Find the threshold wavelength for the metal.
(Use h = 6.63 × 10-34J-s = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, c = 3 × 108 m/s and me = 9.1 × 10-31kg)
The graph shows the variation of photocurrent for a photosensitive metal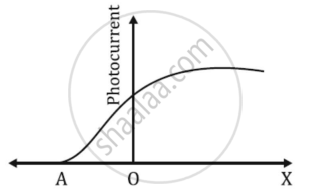
- What does X and A on the horizontal axis represent?
- Draw this graph for three different values of frequencies of incident radiation ʋ1, ʋ2 and ʋ3 (ʋ3 > ʋ2 > ʋ1) for the same intensity.
- Draw this graph for three different values of intensities of incident radiation I1, I2 and I3 (I3 > I2 > I1) having the same frequency.
