Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
- Assertion (A): Work done in moving a charge around a closed path, in an electric field is always zero.
- Reason (R): Electrostatic force is a conservative force.
विकल्प
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is NOT the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Assertion (A) is true and Reason (R) is false.
Assertion (A) is false and Reason (R) is also false.
उत्तर
Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation:
Because the electrostatic force is a conservative force, there is never any work involved in relocating a charge along a closed path in an electric field. A force that conserves mechanical energy is referred to as conservative. The electrostatic force is a force that simply depends on the position of the charges, not their velocity. Therefore, the electrostatic force's effort in transporting a charge along a closed path depends only on the charge's initial and final positions and is independent of the path travelled.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A cube of side b has a charge q at each of its vertices. Determine the potential and electric field due to this charge array at the centre of the cube.
If one of the two electrons of a H2 molecule is removed, we get a hydrogen molecular ion `"H"_2^+`. In the ground state of an `"H"_2^+`, the two protons are separated by roughly 1.5 Å, and the electron is roughly 1 Å from each proton. Determine the potential energy of the system. Specify your choice of zero potential energy.
Four point charges Q, q, Q and q are placed at the corners of a square of side 'a' as shown in the figure.
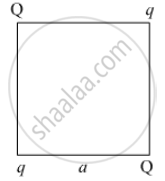
Find the
1) resultant electric force on a charge Q, and
2) potential energy of this system.
A point charge Q is placed at point 'O' as shown in the figure. Is the potential at point A, i.e. VA, greater, smaller or equal to potential, VB, at point B, when Q is (i) positive, and (ii) negative charge?
Figure shows the field lines due to a positive point charge. Give the sign of potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the points Q and P.
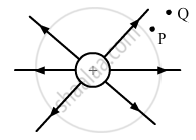
If a charge q0 is there in an electric field caused by several point charges qi. The potential energy of q0 is given by ________.
- Assertion (A): An electron has a high potential energy when it is at a location associated with a more negative value of potential, and a low potential energy when at a location associated with a more positive potential.
- Reason (R): Electrons move from a region of higher potential to region of lower potential.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
In the circuit shown in figure initially, key K1 is closed and key K2 is open. Then K1 is opened and K2 is closed (order is important). [Take Q1′ and Q2′ as charges on C1 and C2 and V1 and V2 as voltage respectively.]

Then
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that V1 = V2
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that Q1′ = Q2′
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that C1V1 + C2V2 = C1E
- charge on C1 gets redistributed such that Q1′ + Q2′ = Q
Calculate potential energy of a point charge – q placed along the axis due to a charge +Q uniformly distributed along a ring of radius R. Sketch P.E. as a function of axial distance z from the centre of the ring. Looking at graph, can you see what would happen if – q is displaced slightly from the centre of the ring (along the axis)?
- In a quark model of elementary particles, a neutron is made of one up quarks [charge (2/3) e] and two down quarks [charges –(1/3) e]. Assume that they have a triangle configuration with side length of the order of 10–15 m. Calculate electrostatic potential energy of neutron and compare it with its mass 939 MeV.
- Repeat above exercise for a proton which is made of two up and one down quark.
