Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Assertion: \[\ce{Cu}\] cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
Reason: Because it has positive electrode potential.
विकल्प
Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion is not true but reason is true.
Both assertion and reason are false.
उत्तर
Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Explanation:
\[\ce{Cu}\] lies below hydrogen in electrochemical series and has positive electrode potential. hence cannot liberate hydrogen from acids.
Both the statements assertion and reason are correct and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why +2 oxidation state of manganese is more stable?
The `E_((M^(2+)//M))^Θ` value for copper is positive (+0.34 V). What is possibly the reason for this? (Hint: consider its high ΔaHΘ and low ΔhydHΘ)
Which metal in the first series of transition metals exhibits +1 oxidation state most frequently and why?
Use Hund’s rule to derive the electronic configuration of Ce3+ ion and calculate its magnetic moment on the basis of ‘spin-only’ formula.
Write the factors which are related to the colour of transition metal ions.
Why do transition metal ions possess a great tendency to form complexes?
Why do transition elements show variable oxidation states ? In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which elements shows the maximum number of oxidation state and why ?
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
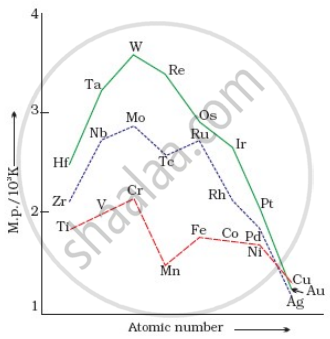
- Why Manganese has lower melting point than Chromium?
- Why do transition metals of 3d series have lower melting points as compared to 4d series?
- In the third transition series, identify and name the metal with the highest melting point.
The orientation of an atomic orbital is governed by
Mercury is the only metal liquid at room temperature due to its:-
