Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write the factors which are related to the colour of transition metal ions.
Write the conditions of colour of transition metal ion.
उत्तर
Factors responsible for colour of a transition metal ions:
- The presence of incompletely filled d – orbitals in metal ions.
- The presence of unpaired electrons in d – orbitals.
- d – d transition of electrons due to absorption of radiation in the visible region.
- Type of hybridisation in metal ion in the complex.
- Geometry of the complex containing transition metal ion.
संबंधित प्रश्न
In 3d series (Sc to Zn), which element has the lowest enthalpy of atomisation and why?
How would you account for the following: Transition metals form complex compounds.
|
`E_((M^(2+)/M)` |
Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu |
| -0.91 | -1.18 | -0.44 | -0.28 | -0.25 | -0.34 |
From the given data of E0 values, answer the following questions :
(1) Why is `E_(((Cu^(2+))/(Cu)))` value exceptionally positive
(2) Why is `E_(((Mn^(2+))/(Mn)))` value is highly negative as compared to other elements
(3) Which is the stronger reducing agents Cr2+ or Fe2+ ? Give Reason.
Explain why Cu+ ion is not stable in aqueous solutions?
In what way is the electronic configuration of the transition elements different from that of the non-transition elements?
An analysis shows that FeO has a non-stoichiometric composition with formula Fe0.95O. Give reason.
Two metallic elements A and B have the following standard oxidation potentials: A = 0·40v B = - 0·80v. What would you expect if element A was added to an aqueous salt solution of element B? Give a reason for your answer.
Why does copper not replace hydrogen from acids?
Out of \[\ce{Cu2Cl2}\] and \[\ce{CuCl2}\], which is more stable and why?
While filling up of electrons in the atomic orbitals, the 4s orbital is filled before the 3d orbital but reverse happens during the ionisation of the atom. Explain why?
Identify A to E and also explain the reactions involved.
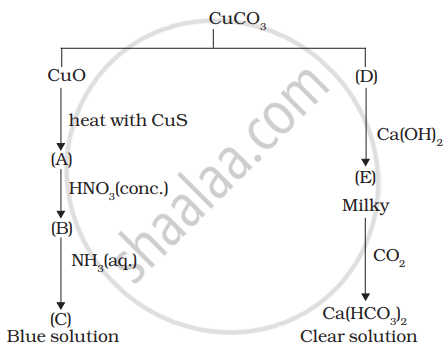
Answer the following question:
Which element of the first transition series has highest second ionisation enthalpy?
Account for the following:
In case of transition elements, ions of the same charge in a given series show progressive decrease in radius with increasing atomic number.
The orientation of an atomic orbital is governed by
The standard electrode potentials of four elements A, B, C and D are – 3.05, – 1.66, – 0.40 and + 0.80. The highest chemical reactivity will be exhibited by
Which does not belong to first transition series?
Mercury is the only metal liquid at room temperature due to its:-
A complex in which dsp2 hybridisation takes place is
Why is the `"E"_(("V"^(3+)//"V"^(2+)))^"o"` value for vanadium comparatively low?
Give reasons for the following statement:
Transition metals and most of their compounds show paramagnetic behaviour.
Give reason for the following statement:
[Ti(H2O)]3+ is coloured while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless.
How is the variability in oxidation states of transition metals different from that of p-block elements?
Which of the following ions acts as a typical transition metal ion?
In the ground state of atomic Fe (Z = 26), the spin-only magnetic moment is ______ × 10-1 BM.
(Round off to the nearest integer).
[Given: `sqrt3 = 1.73, sqrt2 = 1.41`]
The disproportionation of \[\ce{MnO^{2-}_4}\] in acidic medium resulted in the formation of two manganese compounds A and B. If the oxidation state of Mn in B is smaller than that of A, then the spin-only magnetic moment (µ) value of B in BM is ______. (Nearest integer)
The trend of which property is represented by the following graph?
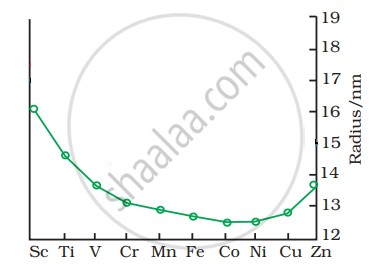
Give two similarities in the properties of Sc and Zn.
Give a reason for the following:
Zinc, cadmium and mercury are considered as d-block elements but not regarded as transition elements.
