Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{P4(s) + OH–(aq) —> PH3(g) + HPO^–_2(aq)}\]
उत्तर
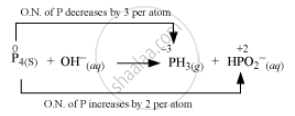
The O.N. (oxidation number) of P decreases from 0 in P4 to –3 in PH3 and increases from 0 in P4 to + 2 in `"HPO"_2^(-)`. Hence, P4 acts both as an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent in this reaction.
Ion-electron method:
The oxidation half equation is:
\[\ce{P4s →HPO2- (aq)}\]
The P atom is balanced as:
\[\ce{P4s →4HPO2- (aq)}\]
The O atom is balanced by adding 8 H2O molecules:
\[\ce{P4s + 8H2O → 4HPO2- (aq)}\]
The H atom is balanced by adding 12 H+ ions:
\[\ce{P4s +8H2O →4HPO2- (aq) + 12H+}\]
The charge is balanced by adding e– as:
\[\ce{P4s +8H2O →4HPO2- (aq) + 12H+ + 8e-}\] ...(i)
The reduction half equation is:
\[\ce{P_{4(s)} -> PH_{3(g)}}\]
The P atom is balanced as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) → 4PH3(g)}\]
The H is balanced by adding 12 H+ as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) + 12H + → 4PH3(g)}\]
The charge is balanced by adding 12e– as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) + 12H+ +12e- → 4PH3(g)}\] ...(ii)
By multiplying equation (i) with 3 and (ii) with 2 and then adding them, the balanced chemical equation can be obtained as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +24H2O →12HPO2^- + 8PH3(g) +12H+}\]
As, the medium is basic, add 12OH– both sides as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +12H2O +12OH- →12HPO2^- +8PH3(g)}\]
This is the required balanced equation.
Oxidation number method:
Let, total no of P reduced = x
∴ Total no of P oxidised = 4 – x
\[\ce{P4 (s) + OH- → xPH3(g) + 4 - xHPO2-}\] ... (i)
Total decrease in oxidation number of P = x × 3 = 3x
Total increase in oxidation number of P
= (4 – x) × 2 = 8 – 2x
∵ 3x = 8 – 2x
x = 8/5
From (i),
\[\ce{5P4 (s) + 5OH- → 8PH3(g) + 12HPO2-}\]
Since, reaction occures in basic medium, the charge is balanced by adding 7OH– on LHS as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +12OH- → 8PH3(g) +12HPO2-}\]
The O atoms are balanced by adding 12H2O as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) + 12H2O + 12OH- → +12HPO2- + 8PH3(g)}\]
This is the required balanced equation.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2(l) → H2O(l) + 2O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2 (l) → H2O(l) + O2(g) + O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
How do you count for the following observations?
Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why? Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction.
Balance the following equation in the basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{N2H4(l) + ClO^-_3 (aq) → NO(g) + Cl–(g)}\]
Justify that the following reaction is redox reaction; identify the species oxidized/reduced, which acts as an oxidant and which acts as a reductant.
\[\ce{2Cu2O_{(S)} + Cu2S_{(S)}->6Cu_{(S)} + SO2_{(g)}}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + Sn(OH)^-_{3(aq)}->Bi_{(s)} + Sn(OH)^2-_{6(aq)}(basic)}\]
Which of the following is INCORRECT for the following reaction?
\[\ce{2Zn_{(s)} + O2_{(g)} -> 2ZnO_{(s)}}\]
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Reaction of liquid hydrazine \[\ce{(N2H4)}\] with chlorate ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}3)}\] in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + S2O^{2-}3 -> I- + S4O^{2-}6}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{3HCl (aq) + HNO3 (aq) -> Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) -> HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) ->[Δ] 2Fe (s) + 3CO2 (g)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) -> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + H^{+} + I- -> Cr^{3+} + I2 + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + Fe^{2+} + H+ -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + SO^{2-}3 + H^{+} -> Mn^{2+} + SO^{2-}4 + H2O}\]
In acidic medium, reaction, \[\ce{MNO^-_4 → Mn^2+}\] an example of ____________.
Consider the following reaction:
\[\ce{xMnO^-_4 + yC2O^{2-}_4 + zH^+ -> xMn^{2+} + 2{y}CO2 + z/2H2O}\]
The values of x, y, and z in the reaction are, respectively:
