Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{P4(s) + OH–(aq) —> PH3(g) + HPO^–_2(aq)}\]
Solution
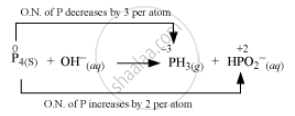
The O.N. (oxidation number) of P decreases from 0 in P4 to –3 in PH3 and increases from 0 in P4 to + 2 in `"HPO"_2^(-)`. Hence, P4 acts both as an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent in this reaction.
Ion-electron method:
The oxidation half equation is:
\[\ce{P4s →HPO2- (aq)}\]
The P atom is balanced as:
\[\ce{P4s →4HPO2- (aq)}\]
The O atom is balanced by adding 8 H2O molecules:
\[\ce{P4s + 8H2O → 4HPO2- (aq)}\]
The H atom is balanced by adding 12 H+ ions:
\[\ce{P4s +8H2O →4HPO2- (aq) + 12H+}\]
The charge is balanced by adding e– as:
\[\ce{P4s +8H2O →4HPO2- (aq) + 12H+ + 8e-}\] ...(i)
The reduction half equation is:
\[\ce{P_{4(s)} -> PH_{3(g)}}\]
The P atom is balanced as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) → 4PH3(g)}\]
The H is balanced by adding 12 H+ as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) + 12H + → 4PH3(g)}\]
The charge is balanced by adding 12e– as:
\[\ce{P4 (s) + 12H+ +12e- → 4PH3(g)}\] ...(ii)
By multiplying equation (i) with 3 and (ii) with 2 and then adding them, the balanced chemical equation can be obtained as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +24H2O →12HPO2^- + 8PH3(g) +12H+}\]
As, the medium is basic, add 12OH– both sides as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +12H2O +12OH- →12HPO2^- +8PH3(g)}\]
This is the required balanced equation.
Oxidation number method:
Let, total no of P reduced = x
∴ Total no of P oxidised = 4 – x
\[\ce{P4 (s) + OH- → xPH3(g) + 4 - xHPO2-}\] ... (i)
Total decrease in oxidation number of P = x × 3 = 3x
Total increase in oxidation number of P
= (4 – x) × 2 = 8 – 2x
∵ 3x = 8 – 2x
x = 8/5
From (i),
\[\ce{5P4 (s) + 5OH- → 8PH3(g) + 12HPO2-}\]
Since, reaction occures in basic medium, the charge is balanced by adding 7OH– on LHS as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) +12OH- → 8PH3(g) +12HPO2-}\]
The O atoms are balanced by adding 12H2O as:
\[\ce{5P4 (s) + 12H2O + 12OH- → +12HPO2- + 8PH3(g)}\]
This is the required balanced equation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` and `"NO"_3^-`. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2(l) → H2O(l) + 2O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{O3(g) + H2O2 (l) → H2O(l) + O2(g) + O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
The compound AgF2 is an unstable compound. However, if formed, the compound acts as a very strong oxidizing agent. Why?
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{Cl_2O_{7(g)} + H_2O_{2(aq)} -> ClO-_{2(aq)} + O_{2(g)} + H+_{(aq)}}\]
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2, and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Cr2O^2-_{7(aq)} + SO^2-_{3(aq)}->Cr^3+_{ (aq)} + SO^2-_{4(aq)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + Sn(OH)^-_{3(aq)}->Bi_{(s)} + Sn(OH)^2-_{6(aq)}(basic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)} + MnO^-_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)} + Mn^2+_{( aq)}(acidic)}\]
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
What is the change in oxidation number of Sulphur in following reaction?
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{3(aq)} -> MnO^{2-}_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}}\]
Identify the oxidising agent in the following reaction:
\[\ce{CH4_{(g)} + 2O2_{(g)} -> CO2_{(g)} + 2H2O_{(l)}}\]
When methane is burnt completely, oxidation state of carbon changes from ______.
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{Fe2O3 (s) + 3CO (g) ->[Δ] 2Fe (s) + 3CO2 (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
In \[\ce{Cu^{2+} + Ag -> Cu + Ag^+}\], oxidation half-reaction is:
In the reaction of oxalate with permanganate in an acidic medium, the number of electrons involved in producing one molecule of CO2 is ______.
