Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Solution
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Step 1: Write the skeletal equation and balance the elements other than O and H.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 2: Assign oxidation number to S and C. Calculate the increase and decrease in the oxidation number and make them equal.
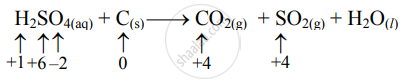
Increase in oxidation number:

(Increase per atom = 4)
Decrease in oxidation number:
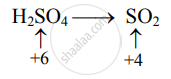
(Decrease per atom = 2)
To make the net increase and decrease equal, we must take 2 atoms of S.
\[\ce{2H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + 2SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 3: Balance ‘O’ atoms by adding H2O to the right-hand side.
\[\ce{2H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + 2SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)} + H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 4: The medium is acidic. There is no charge on either side. Hydrogen atoms are equal on both sides.
\[\ce{2H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + 2SO2_{(g)} + 2H2O_{(l)}}\]
Step 5: Check two sides for the balance of atoms and charges.
Hence, balanced equation: \[\ce{2H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + 2SO2_{(g)} + 2H2O_{(l)}}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` and `"NO"_3^-`. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
How do you count for the following observations?
Though alkaline potassium permanganate and acidic potassium permanganate both are used as oxidants, yet in the manufacture of benzoic acid from toluene we use alcoholic potassium permanganate as an oxidant. Why? Write a balanced redox equation for the reaction.
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{P4(s) + OH–(aq) —> PH3(g) + HPO^–_2(aq)}\]
In Ostwald’s process for the manufacture of nitric acid, the first step involves the oxidation of ammonia gas by oxygen gas to give nitric oxide gas and steam. What is the maximum weight of nitric oxide that can be obtained starting only with 10.00 g. of ammonia and 20.00 g of oxygen?
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + Br^-_{ (aq)}->MnO2_{ (s)} + BrO^-_{3(aq)}(basic)}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + Sn(OH)^-_{3(aq)}->Bi_{(s)} + Sn(OH)^2-_{6(aq)}(basic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{H2C2O_{4(aq)} + MnO^-_{4(aq)}->CO2_{(g)} + Mn^2+_{( aq)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following redox equation by half-reaction method.
\[\ce{Bi(OH)_{3(s)} + SnO^2-_{2(aq)}->SnO^2-_{3(aq)} + Bi^_{(s)}(basic)}\]
Identify coefficients 'x' and 'y' for the following reaction.
\[\ce{{x}H2O2_{(aq)} + ClO^-_{4(aq)} -> 2O2_{(g)} + ClO^-_{2(aq)} + {y}H2O_{(l)}}\]
Which of the following is a redox reaction?
When methane is burnt completely, oxidation state of carbon changes from ______.
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Write balanced chemical equation for the following reactions:
Reaction of liquid hydrazine \[\ce{(N2H4)}\] with chlorate ion \[\ce{(ClO^{-}3)}\] in basic medium produces nitric oxide gas and chloride ion in gaseous state.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + S2O^{2-}3 -> I- + S4O^{2-}6}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO2 + C2O^{2-}4 -> Mn^{2+} + CO2}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{3HCl (aq) + HNO3 (aq) -> Cl2 (g) + NOCl (g) + 2H2O (l)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{HgCl2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) -> HgI2 (s) + 2KCl (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) -> 3HCl (aq) + H3PO3 (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) -> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{Cr2O^{2-}7 + Fe^{2+} + H+ -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + SO^{2-}3 + H^{+} -> Mn^{2+} + SO^{2-}4 + H2O}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + H^{+} + Br^{-} -> Mn^{2+} + Br2 + H2O}\]
In the reaction of oxalate with permanganate in an acidic medium, the number of electrons involved in producing one molecule of CO2 is ______.
