Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the focal length of a corrective lens having power +2D.
उत्तर
Given: Focal length f = +2 D
Power ,p=1/f
∴f=1/p=1/2
∴f=0.5m
The power of the corrective lens is 0.5 m.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the focal length of a corrective lens having power +2.5 D.
Define the power of a lens.
Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2m.
Find the focal length of a lens of power −2.0 D. What type of lens is this?
What is the focal length of a convex lens of focal length 30 cm in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm? Is the system a converging or a diverging lens? Ignore thickness of the lenses.
You have two lenses A and B of focal lengths +10 cm and –10 cm, respectively. State the nature and power of each lens. Which of the two lenses will form a virtual and magnified image of an object placed 8 cm from the lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer
The lens mentioned in 6(b) above is of focal length 25cm. Calculate the power of the lens.
A student uses a lens of focal length 40 cm and another of –20 cm. Write the nature and power of each lens
How is the power of a lens related to its focal length?
Which has more power : a thick convex lens or a thin convex lens, made of the same glass? Give reason for your choice.
The focal length of a convex lens is 25 cm. What is its power?
A converging lens has focal length of 50 mm. What is the power of the lens?
What is the power of a convex lens lens whose focal length is 80 cm?
A diverging lens has focal length of 3 cm. Calculate the power.
The power of a lens is + 0.2 D. Calculate its focal length.
The focal length of a lens is +150 mm. What kind of lens is it and what is its power?
Two lenses A and B have focal lengths of +20 cm and, −10 cm, respectively.
(a) What is the nature of lens A and lens B?
(b) What is the power of lens A and lens B?
(c) What is the power of combination if lenses A and B are held close together?
A converging lens has a focal length of 50 cm. The power of this lens is:
State the condition for the following a lens has both its focal lengths equal .
State the condition for the following a ray passes undeviated through the lens .
How is the power of a lens related to its focal length?
The power of a lens is + 1.0 D is :
Define power of a lens. Write its units. Deduce the relation `1/f =1/f_1 +1/f_2`for two thin lenses kept in contact coaxially.
A normal eye is not able to see objects closer than 25 cm because
A thin converging lens is formed with one surface convex and the other plane. Does the position of image depend on whether the convex surface or the plane surface faces the object?
A double convex lens has two surfaces of equal radii R and refractive index \[m = 1 \cdot 5\]
A symmetric double convex lens is cut in two equal parts by a plane containing the principal axis. If the power of the original lens was 4 D, the power of a divided lens will be
Consider three converging lenses L1, L2 and L3 having identical geometrical construction. The index of refraction of L1 and L2 are \[\mu_1 \text{ and } \mu_2\] respectively. The upper half of the lens L3 has a refractive index \[\mu_1\] and the lower half has \[\mu_2\] following figure . A point object O is imaged at O1 by the lens L1 and at O2 by the lens L2placed in same position. If L3 is placed at the same place,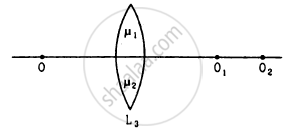
(a) there will be an image at O1
(b) there will be an image at O2.
(c) the only image will form somewhere between O1 and O2
(d) the only image will form away from O2.
A double convex lens has focal length 25 cm. The radius of curvature of one of the surfaces is double of the other. Find the radii, if the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
A convex lens produces a double size real image when an object is placed at a distance of 18 cm from it. Where should the object be placed to produce a triple size real image?
According to Rayleigh’s scattering law, the amount of scattering of light is inversely proportional to the fourth power of its ______.
Increase in the converging power of eye lens cause ‘hypermetropia'
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II | ||
| 1 | Retina | a | Path way of light |
| 2 | Pupil | b | Far point comes closer |
| 3 | Ciliary muscles | c | near point moves away |
| 4 | Myopia | d | Screen of the eye |
| 5 | Hypermetropia | e | Power of accommodation |

The above lens has a focal length of 10 cm. The object of height 2 mm is placed at a distance of 5 cm from the pole. Find the height of the image.
The power of convex lens of focal length 20 cm is ______.
