Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the oxidation number of sulphur, chromium and nitrogen in H2SO5, `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` and `"NO"_3^-`. Suggest structure of these compounds. Count for the fallacy.
उत्तर
1)
+1 x -2
\[\ce{H2SO5}\]
2(+1) + 1(x) + 5(-2) = 0
⇒ 2 + x - 10 = 0
⇒ x = + 8
However, the O.N. of S cannot be +8. S has six valence electrons. Therefore, the O.N. of S cannot be more than +6.
The structure of H2SO5 is shown as follows:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{^{-2}O}\phantom{...........}\\
||\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{^{+1}H - ^{-2}O - S^{\text{x}} - ^{-1}O - ^{-1}O - ^{+1}H}\\
||\phantom{.........}\\
\ce{^{-2}O}\phantom{............}\end{array}\]
Now, 2(+1) + 1(x) + 3(-2) + 2(-1) = 0
⇒ 2 + x - 6 - 2 = 0
⇒ x = +6
Therefore, the O.N. of S is +6.
2)
x 2-
\[\ce{Cr2 O^{2-}_7}\]
2(x) + 7(-2) = -2
⇒ 2x - 14 = -2
⇒ x = +6
Here, there is no fallacy about the O.N. of Cr in `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)`.
The structure of `"Cr"_2"O"_7^(2-)` is shown as follows:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{^{2-}O}\phantom{...........}\ce{^{2-}O}\phantom{....}\\
||\phantom{..............}||\phantom{..}\\
\ce{^{2-}O = Cr^{+6} - ^{2-}O - Cr^{+6} - O^{2-}}\\
|\phantom{..............}|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{_{1-}O^-}\phantom{.........}\ce{_{1-}O^-}\phantom{....}\end{array}\]
Here, each of the two Cr atoms exhibits the O.N. of +6.
3)
x 2-
\[\ce{N O^-_3}\]
1(x) + 3(-2) = -1
⇒ x - 6 = -1
⇒ x = +5
Here, there is no fallacy about the O.N. of N in `"NO"_3^(-)`
The structure of `"NO"_3^(-)` is shown as follows
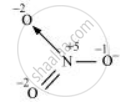
The N atom exhibits the O.N. of +5.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Balance the following equation in basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{P4(s) + OH–(aq) —> PH3(g) + HPO^–_2(aq)}\]
Balance the following equation in the basic medium by ion-electron method and oxidation number methods and identify the oxidising agent and the reducing agent.
\[\ce{N2H4(l) + ClO^-_3 (aq) → NO(g) + Cl–(g)}\]
The Mn3+ ion is unstable in solution and undergoes disproportionation to give Mn2+, MnO2, and H+ ion. Write a balanced ionic equation for the reaction.
Chlorine is used to purify drinking water. Excess of chlorine is harmful. The excess of chlorine is removed by treating with sulphur dioxide. Present a balanced equation for this redox change taking place in water.
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Cr2O^2-_{7(aq)} + SO^2-_{3(aq)}->Cr^3+_{ (aq)} + SO^2-_{4(aq)}(acidic)}\]
Balance the following reaction by oxidation number method.
\[\ce{H2SO4_{(aq)} + C_{(s)}->CO2_{(g)} + SO2_{(g)} + H2O_{(l)}(acidic)}\]
Identify coefficients 'x' and 'y' for the following reaction.
\[\ce{{x}H2O2_{(aq)} + ClO^-_{4(aq)} -> 2O2_{(g)} + ClO^-_{2(aq)} + {y}H2O_{(l)}}\]
What is the change in oxidation number of Sulphur in following reaction?
\[\ce{MnO^-_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{3(aq)} -> MnO^{2-}_{4(aq)} + SO^{2-}_{4(aq)}}\]
Consider the reaction:
\[\ce{6 CO2(g) + 6H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)}\]
Why it is more appropriate to write these reaction as:
\[\ce{6CO2(g) + 12H2O(l) → C6 H12O6(aq) + 6H2O(l) + 6O2(g)}\]
Also, suggest a technique to investigate the path of the redox reactions.
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{Fe^{2+} + H^{+} + Cr2O^{2-}7 -> Cr^{3+} + Fe^{3+} + H2O}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{I2 + S2O^{2-}3 -> I- + S4O^{2-}6}\]
Balance the following equations by the oxidation number method.
\[\ce{MnO2 + C2O^{2-}4 -> Mn^{2+} + CO2}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{PCl3 (l) + 3H2O (l) -> 3HCl (aq) + H3PO3 (aq)}\]
Identify the redox reactions out of the following reactions and identify the oxidising and reducing agents in them.
\[\ce{4NH3 (g) + 3O2 (g) -> 2N2 (g) + 6H2O (g)}\]
Balance the following ionic equations.
\[\ce{MnO^{-}4 + SO^{2-}3 + H^{+} -> Mn^{2+} + SO^{2-}4 + H2O}\]
The weight of CO is required to form Re2(CO)10 will be ______ g, from 2.50 g of Re2O7 according to given reaction
\[\ce{Re2O7 + CO -> Re2(CO)10 + CO2}\]
Atomic weight of Re = 186.2; C = 12 and O = 16.
In the reaction of oxalate with permanganate in an acidic medium, the number of electrons involved in producing one molecule of CO2 is ______.
