Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Calculate the total number of angular nodes and radial nodes present in 3p orbital.
उत्तर
The number of radial nodes is given by n – l – 1,where n is principal quantum number, l is azimuthal quantum number.
The number of angular nodes is given by n – l, where n is principal quantum number, l is azimuthal quantum number.
Here n = 3 and l = 1
Thus, angular nodes = 3 – 1 = 2 and radial node = 3 – 1 – 1 = 1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Using s, p, d notations, describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers n = 1, l = 0.
Using s, p, d notations, describe the orbital with the following quantum numbers n = 3; l =1.
Choose the correct option.
p-orbitals are _________ in shape.
Choose the correct option.
“No two electrons in the same atoms can have identical set of four quantum numbers”. This statement is known as -
State and explain Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Chlorine (Z = 17)
Write condensed orbital notation of electronic configuration of the following element:
Calcium (Z = 20)
Explain in brief, the significance of the azimuthal quantum number.
The probability density plots of 1s and 2s orbitals are given in Figure:
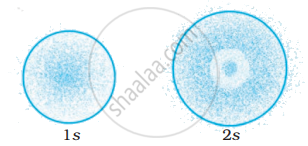
The density of dots in a region represents the probability density of finding electrons in the region.
On the basis of above diagram which of the following statements is incorrect?
Match the following species with their corresponding ground state electronic configuration.
| Atom / Ion | Electronic configuration |
| (i) \[\ce{Cu}\] | (a) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 |
| (ii) \[\ce{Cu^{2+}}\] | (b) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 |
| (iii) \[\ce{Zn^{2+}}\] | (c) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s1 |
| (iv) \[\ce{Cr^{3+}}\] | (d) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d9 |
| (e) 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d3 |
