Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Can an electromagnetic wave be polarised?
उत्तर
An electromagnetic wave is a transverse wave; thus, it can be polarised. An unpolarised wave consists of many independent waves, whose planes of vibrations of electric and magnetic fields are randomly oriented. They are polarised by restricting the vibrations of the electric field vector or magnetic field vector in one direction only.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How are electromagnetic waves produced?
Identify the electromagnetic waves whose wavelengths vary as:
(a) 10–12 m < λ < 10–8 m
(b) 10–3 m < λ < 10–1 m
Write one use for each.
A plane electromagnetic wave is travelling through a medium along the +ve z-direction. Depict the electromagnetic wave showing the directions of the oscillating electric and magnetic fields.
Which segment of electromagnetic waves has highest frequency? How are these waves produced? Give one use of these waves.
How does a charge q oscillating at certain frequency produce electromagnetic waves?
Sketch a schematic diagram depicting electric and magnetic fields for an electromagnetic wave propagating along the Z-direction.
A plane electromagnetic wave is passing through a region. Consider (a) electric field (b) magnetic field (c) electrical energy in a small volume and (d) magnetic energy in a small volume. Construct the pairs of the quantities that oscillate with equal frequencies.
The electric and magnetic fields, associated with an electromagnetic wave, propagating along negative X-axis can be represented by ______.
Which one of them is used to produce a propagating electromagnetic wave?
Write down Maxwell equations in integral form.
Write a short note on the radio waves.
A pulse of light of duration 10-6 s is absorbed completely by a small object initially at rest. If the power of the pulse is 60 x 10-3 W, calculate the final momentum of the object.
The electric field of a plane electromagnetic wave travelling in +ve z-direction is described by ______.
Dimensions of ε0 `(d phi_ε)/(dt)` are of
For which frequency of light, the eye is most sensitive?
An EM wave radiates outwards from a dipole antenna, with E0 as the amplitude of its electric field vector. The electric field E0 which transports significant energy from the source falls off as ______.
An EM wave of intensity I falls on a surface kept in vacuum and exerts radiation pressure p on it. Which of the following are true?
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally absorbed.
- Radiation pressure is `I/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is `(2I)/c` if the wave is totally reflected.
- Radiation pressure is in the range `I/c < p < (2I)/c` for real surfaces.
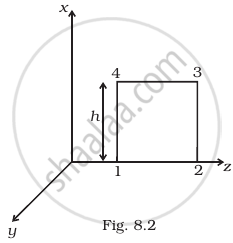
A plane EM wave travelling in vacuum along z direction is given by `E = E_0 sin(kz - ωt)hati` and `B = B_0 sin(kz - ωt)hatj`
- Evaluate `oint E.dl` over the rectangular loop 1234 shown in figure.
- Evaluate `int B.ds` over the surface bounded by loop 1234.
- Use equation `oint E.dl = (-dphi_B)/(dt)` to prove `E_0/B_0` = c.
- By using similar process and the equation `ointB.dl = mu_0I + ε_0 (dphi_E)/(dt)`, prove that c = `1/sqrt(mu_0ε_0)`
A plane electromagnetic wave, has frequency of 2.0 × 1010 Hz and its energy density is 1.02 × 10-8 J/m3 in vacuum. The amplitude of the magnetic field of the wave is close to `(1/(4piepsilon_0) = 9xx10^9"Nm"^2/"C"^2 "and speed of light" = 3 xx 10^8 "m" "s"^-1)`:
Sunlight falls normally on a surface of area 36 cm2 and exerts an average force of 7.2 × 10-9 N within a time period of 20 minutes. Considering a case of complete absorption the energy flux of incident light is ______.
The diagram below shows the electric field (E) and magnetic field (B) components of an electromagnetic wave at a certain time and location.

The direction of the propagation of the electromagnetic wave is ______.
