Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
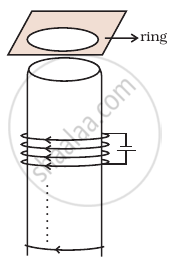
Consider a metal ring kept (supported by a cardboard) on top of a fixed solenoid carrying a current I (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is switched off, what will happen to the ring?

उत्तर
This problem is based on Lenz’s law and according to this law, the direction of induced emf or current in a circuit is such as to oppose the cause that produces it.
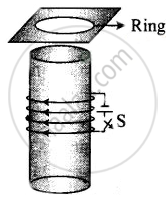
When the switch is opened, current in the circuit of solenoid stops flowing. Initially, there is some magnetic flux linked with the solenoid and now if current in the circuit stops, the magnetic flux falls to zero or we can say that magnetic flux linked through the ring decreases.
According to Lenz’s law, this decrease in flux will be opposed and the ring experiences downward force toward the solenoid.
This happen because the current decrease will cause a clockwise current (as seen from the top in the ring in figure) to increase the decreasing flux. This can be done if the direction of induced magnetic field is same as that of solenoid. This makes the opposite sense of the flow of current in the ring (when viewed from the bottom of the ring) and solenoid form opposite magnetic poles in front of each other.
Hence, they will -attract each other but as ring is placed at the cardboard it could not be able to move downward.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
Describe a simple experiment (or activity) to show that the polarity of emf induced in a coil is always such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change of magnetic flux that produces it.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
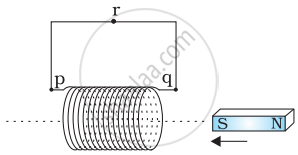
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
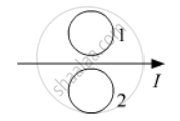
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
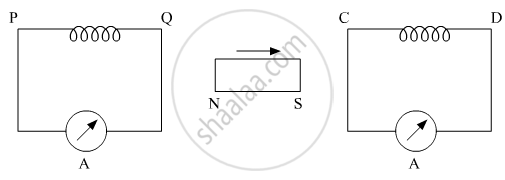
A bar magnet is released from rest along the axis of a very long, vertical copper tube. After some time the magnet ____________ .
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a carboard) (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain
A long solenoid ‘S’ has ‘n’ turns per meter, with diameter ‘a’. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of ‘N’ turns and diameter ‘b’ (where b < a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2 + C.
A coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the coil parallel to the magnetic lines of force. When a current is passed through the coil it starts oscillating: It is very difficult to stop. But if an aluminium plate is placed near to the coil, it stops. This is due to:
