Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a point at the focal point of a convergent lens. Another convergent lens of short focal length is placed on the other side. What is the nature of the wavefronts emerging from the final image?
उत्तर
Orientation of wavefront is perpendicular to ray. The ray diagram of the situation is shown in figure.
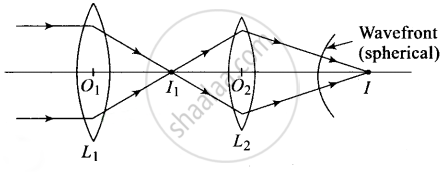
Parallel rays incident on lens L1 forms the image I2 at the focal point of the lens. This image acts as object for the lens L2 Now, due to the converging lens L2 , let final image formed is I which is point image. Hence the wavefront for this image will be of spherical symmetry.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light diverging from a point source.
What is the shape of the wavefront in the following case?
Light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
You have learnt in the text how Huygens’ principle leads to the laws of reflection and refraction. Use the same principle to deduce directly that a point object placed in front of a plane mirror produces a virtual image whose distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror.
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
Using Huygens’ principle, verify the laws of reflection at a plane surface.
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
Two light beams of intensities in the ratio of 9 : 4 are allowed to interfere. The ratio of the intensity of maxima and minima ______.
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
Using Huygen's wave theory of light, show that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Draw a neat and labelled diagram.
What type of wavefronts are associated with a point source of light?
