Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
विकल्प
a and b
a and c
b and c
c and d
उत्तर
a and b
Explanation:
| Type of wavefront | Intensity | Amplitude |
Spherical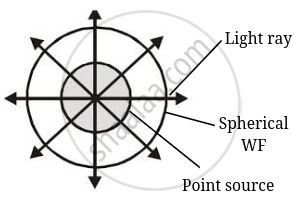 |
`I oo 1/r^2` | `A oo 1/r` |
Cylindrical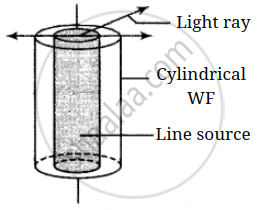 |
`I oo 1/r` | `A oo 1/sqrt(r)` |
Plane |
`I oo 1/r^0` | `A oo r^0` |
Due to the point source light propagates in all directions symmetrically and hence, wavefront will be spherical as shown in the diagram.
As intensity of the source will be `I oo 1/r^2`
Where r is radius of the wavefront at any time.
Hence the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider a plane wave front incident on a thin convex lens. Draw a proper diagram to show how the incident wave front traverses through the lens and after refraction focusses on the focal point of the lens, giving the shape of the emergent wave front.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Define the term wavefront. Using Huygen’s wave theory, verify the law of reflection.
What is the phase difference between any two points lying on the same?
Wavefront means
Huygen's conception of secondary waves ______.
Is Huygen’s principle valid for longitudinal sound waves?
What is the shape of the wavefront on earth for sunlight?
How is a wavefront different from a ray?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
