Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
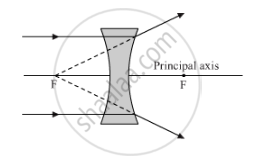
Copy and complete the diagram below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through the concave lens:
उत्तर
The rays will diverge and appear to meet at the focus of the lens.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain with the help of a diagram, why the concave lens is also called a diverging lens.
State one practical use each of convex mirror, concave mirror, convex lens and concave lens.
An object 60 cm from a lens gives a virtual image at a distance of 20 cm in front of the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? Is the lens converging or diverging? Give reasons for your answer.
Calculate the image distance for an object of height 12 mm at a distance of 0.20 m from a concave lens of focal length 0.30 m, and state the nature and size of the image.
The power of a converging lens is 4.5 D and that of a diverging lens is 3 D. The power of this combination of lenses placed close together is :
(a) +1.5D
(b) +7.5D
(c) −7.5D
(d) −1.5D
A concave lens forms the image of an object which is ______.
An object is placed at a distance 24 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 8 cm.
(i) What is the nature of the image so formed?
(ii) Calculate the distance of the image from the lens.
(iii) Calculate the magnification of the image.
Define the term principal foci as applied to a concave lens. Illustrate your answer with the aid of proper diagrams. Show the focal length of the lens in the diagram.
Identify the device used as a spherical mirror or lens in following case, when the image formed is virtual and erect in case.
Object is placed between infinity and device, image formed is diminished and between focus and optical centre on the same side as that of the object.
The focal length of a lens is negative. In this case, state the kind of lens.
