Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the capacitance of a capacitor. Obtain the expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor in vacuum in terms of plate area A and separation d between the plates.
उत्तर
The capacitance of a capacitor is the amount of charge which creates unit potential difference between collecting plate and condensing plate after giving charge on the collecting plate.
Parallel Plate Capacitor
-
A parallel plate capacitor consists of two large plane parallel conducting plates separated by a small distance.

-
Let A be the area of each plate and d the separation between them. The two plates have charges Q and −Q.
-
Surface charge density of plate 1, σ = Q/A, and that of plate 2 is σ.
-
Electric field in different regions:
Outer region I,
`E = σ/(2ε_0) - σ/(2ε_0 ) = 0`
In the inner region between plates 1 and 2, the electric fields due to the two charged plates add up. So,
\[E = \frac{\sigma}{2 \epsilon_0} + \frac{\sigma}{2 \epsilon_0} = \frac{\sigma}{\epsilon_0} = \frac{Q}{\epsilon_0 A}\]
E=σ2ε0+σ2ε0=σε0=Qε0
-
The direction of electric field is from the positive to the negative plate.
-
For uniform electric field, potential difference is simply the electric field multiplied by the distance between the plates, i.e.
`V=Ed = 1/c (Qd)/A`
Capacitance C of the parallel plate capacitor in vacuum is
`C = Q/V =(ε_0A)/d `
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a neat labelled diagram of a parallel plate capacitor completely filled with dielectric.
Explain briefly the process of charging a parallel plate capacitor when it is connected across a d.c. battery
Considering the case of a parallel plate capacitor being charged, show how one is required to generalize Ampere's circuital law to include the term due to displacement current.
A parallel plate capacitor is to be designed with a voltage rating 1 kV, using a material of dielectric constant 3 and dielectric strength about 107 Vm−1. (Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can tolerate without breakdown, i.e., without starting to conduct electricity through partial ionisation.) For safety, we should like the field never to exceed, say 10% of the dielectric strength. What minimum area of the plates is required to have a capacitance of 50 pF?
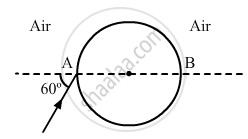
A ray of light falls on a transparent sphere with centre C as shown in the figure. The ray emerges from the sphere parallel to the line AB. Find the angle of refraction at A if the refractive index of the material of the sphere is \[\sqrt{3}\].
A parallel-plate capacitor with plate area 20 cm2 and plate separation 1.0 mm is connected to a battery. The resistance of the circuit is 10 kΩ. Find the time constant of the circuit.
A parallel-plate capacitor is filled with a dielectric material of resistivity ρ and dielectric constant K. The capacitor is charged and disconnected from the charging source. The capacitor is slowly discharged through the dielectric. Show that the time constant of the discharge is independent of all geometrical parameters like the plate area or separation between the plates. Find this time constant.
Solve the following question.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery to a potential difference V. It is disconnected from the battery and then connected to another uncharged capacitor of the same capacitance. Calculate the ratio of the energy stored in the combination to the initial energy on the single capacitor.
In a parallel plate capacitor, the capacity increases if ______.
Two charges – q each are separated by distance 2d. A third charge + q is kept at mid point O. Find potential energy of + q as a function of small distance x from O due to – q charges. Sketch P.E. v/s x and convince yourself that the charge at O is in an unstable equilibrium.
