Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Define the following as related to proteins
Peptide linkage
उत्तर १
The amide formed between −COOH group of one molecule of an amino acid and −NH2 group of another molecule of the amino acid by the elimination of a water molecule is called a peptide linkage
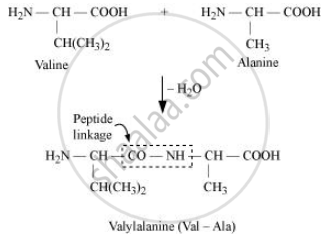
उत्तर २
Peptide bond: Proteins are condensation polymers of α-amino acids in which the same or different α-amino acids are joined by peptide bonds. Chemically, a peptide bond is an amide linkage formed between – COOH group of one α-amino acid and -NH-, group of the other α-amino acid by loss of a molecule of water. For example,

APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the ∝-helix structure of proteins?
Differentiate between the following :
Fibrous proteins and Globular proteins
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water?
The correct statement for protein haemoglobin.
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
The main structural feature of proteins is
Peptide linkage is:
Explain formation of peptide linkage in protein with an example.
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Write a classification of proteins with an example.
