Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Derive the expression for force per unit length between two long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Hence define one ampere.
उत्तर
Two long parallel conductors a and b separated by a distance l and carrying currents Ia and Ib respectively are shown below.

By Ampere’s circuital law, we have
`B_a = (mu_0I_a)/(2pid)`
Conductor b will experience a sideways force because of conductor a. Let this force be Fba.
`F_(b_a) = I_bLB_a` (F =ILB)
`= (mu_0I_aI_bL)/(2pid)`
By symmetry,
Fba = − Fab
1 ampere is the value of that steady current which when maintained in each of the two very long, straight, parallel conductors of negligible cross section and placed one metre apart in vacuum, would produce on each of these conductors a force equal to 2 × 10−7 Newton per metre of length.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An electron is moving along the positive x-axis. You want to apply a magnetic field for a short time so that the electron may reverse its direction and move parallel to the negative x-axis. This can be done by applying the magnetic field along
(a) y-axis
(b) z-axis
(c) y-axis only
(d) z-axis only
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
A current of 10 A is established in a long wire along the positive z-axis. Find the magnetic field \[\vec{B}\] at the point (1 m, 0, 0).
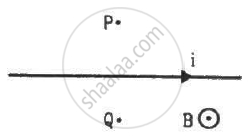
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 1.0 A is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.0 × 10−5 T pointing vertically upward figure. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at the points P and Q, both situated at a distance of 2.0 cm from the wire in the same horizontal plane.
A rectangular coil of 100 turns has length 5 cm and width 4 cm. It is placed with its plane parallel to a uniform magnetic field and a current of 2 A is sent through the coil. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B if the torque acting on the coil is 0.2 N m−1
Two parallel wires carry equal currents of 10 A along the same direction and are separated by a distance of 2.0 cm. Find the magnetic field at a point which is 2.0 cm away from each of these wires.
Two long, straight wires, each carrying a current of 5 A, are placed along the x- and y-axis respectively. The currents point along the positive directions of the axes. Find the magnetic fields at the points (a) (1 m, 1 m), (b) (−1 m, 1 m), (c) (−1 m, −1 m) and (d) (1 m, −1 m).
Consider a 10-cm long piece of a wire which carries a current of 10 A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the piece at a point which makes an equilateral triangle with the ends of the piece.
According to Ampere's circuital law, ______.
A milli voltmeter of 25 milli volt range is to be converted into an ammeter of 25 ampere range. The value (in ohm) of necessary shunt will be ______.
