Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe Rayleigh's criterion for resolution. Explain it for a telescope and a microscope.
उत्तर
Rayleigh's criterion for minimum resolution:
When the centre of one diffraction pattern's central peak is as far as the initial minimum of the other pattern, two overlapping diffraction patterns attributable to two point sources are acceptable or just resolved.
The angular separation between the centre of the peak and the first minimum of a diffraction pattern is used to determine the 'sharpness' of the central maximum. It indicates the resolution's upper limit.
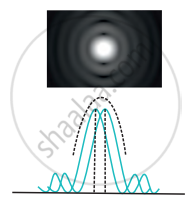 |
 |
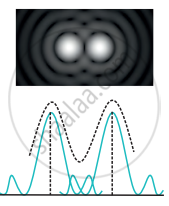 |
| (a) Unresolved | (b) Just resolved | (c) well resolved |
If the angular separation between the central peaks is less than the limit of resolution in the first figure, two overlapping diffraction patterns caused by two point sources cannot be resolved. If the angular separation between the central peaks equals the limit of resolution in the second figure, they are said to be just separate or resolved. If the angular separation between the central peaks is greater than the limit of resolution in the third figure, they are said to be well resolved.
Resolving power of an optical instrument:
Whether looking at a star system through a telescope or a living cell through a microscope, the basic goal of utilising an optical device is to discern small details. Light from two adjacent parts of the object should produce sharp, distinct (separate) images of those parts after passing through an optical system. The objective lens or mirror of a telescope or microscope acts like a circular aperture. A circular aperture's diffraction pattern is composed of a central bright spot (called the Airy disc and corresponds to the central maximum) and concentric dark and bright rings. After passing through the aperture of an optical system, light from two close objects or parts of an object produces overlapping diffraction patterns that tend to obscure the image. If these diffraction patterns are so broad that their central maxima significantly overlap, it is difficult to determine whether the intensity distribution is produced by two separate objects or by one. The ability of an optical instrument, such as a telescope or microscope, to produce detectably separate images of objects that are packed together is measured by its resolving power.
Definition: The smallest linear or angular separation between two point objects that appear just resolved when viewed through an optical instrument is known as the instrument's limit of resolution, and its reciprocal is known as the instrument's resolving power.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The resolving power of a telescope depends upon the ______.
If numerical aperture of a microscope is increased, then its ______.
Describe Young’s double-slit experiment with a neat diagram showing points of maximum and minimum intensity.
An object is clearly seen through an astronomical telescope of length 50 cm. The focal lengths of its objective and eye-piece respectively can be ______.
By increasing the aperture of the objective lens, wavelength of light, focal length of the objective lens and the resolving power of an astronomical telescope respectively.
A telescope has large diameter of the objective. Then its resolving power is ______.
If the mass of a body is m on the surface of the earth, the mass of the same body on the surface of the moon is ______.
When sunlight is scattered by atmospheric atoms and molecules, the amount of scattered light, of wavelength 440 nm, is 'I'. What amount of light of wavelength 660 nm will be scattered?
When wavelength of light used in optical instruments A and B are 4500 Å and 6000 Å respectively, the ratio of resolving power of A to B will be ______.
According to Abbe, in the formula for resolving power of a microscope, the numerical aperture is represented by ______
The aperture of the objective is 24.4 cm. The resolving power of this telescope. If a light of wavelength 2440 Å is used to see the object will be ______.
Wavelength of light used in an optical instrument are λ1 = 4000 Å and λ2 = 5000 Å, then ratio of their respective resolving powers (corresponding to λ1 and λ2) is ______.
Resolving power of telescope increases when ______.
Which of the following would permit finer detail to be examined using a microscope of a given numerical aperture?
Determine the limit of resolution of a telescope for the light of wavelength 500 nm if the telescope objective has diameter of 5.08 m.
Define the resolving power of a telescope.
State the formula for resolving the power of a telescope.
What is the resolving power of telescope if the diameter of the objective of the telescope is 1.22 m and the wavelength of light is sooo A?
