Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the construction and working of a transformer with a neat labelled diagram.
Explain the working of a transformer with a neat, labelled diagram.
उत्तर
Principle:
It is based on the principle of mutual induction, i.e., whenever the magnetic flux linked with a coil changes, an e.m.f is induced in the neighbouring coil.
- Construction:
a. A transformer consists of two sets of coils, primary P and secondary S, insulated from each other. Coil P is called the input coil, and coil S is called the output coil.
b. The two coils are wound separately on a laminated soft iron core.
- Working:
a. When an alternating voltage is applied to the primary coil, the current through the coil goes on changing. Hence, the magnetic flux through the core also changes.
b. As this changing magnetic flux is linked with both the coils, an e.m.f is induced in each coil.
c. The amount of the magnetic flux linked with the coil depends upon the number of turns of the coil.
d. Let, ‘Φ’ be the magnetic flux linked per turn with both the coils at a certain instant ‘t’.
e. Let ‘NP' and ‘NS’ be the number of turns of the primary and secondary coil,
NPΦ = magnetic flux linked with the primary coil at a certain instant ‘t’
NSΦ = magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil at a certain instant ‘t’
f. Induced e.m.f produced in the primary and secondary coil is given by,
`"e"_"p" = -("d"phi_"p")/"dt" = -"N"_"p"("d"phi)/"dt"` ….(1)
`"e"_"s" = -("d"phi_"s")/"dt" = -"N"_"s"("d"phi)/"dt"` ….(2)
g. Dividing equation (2) by (1),
∴ `"e"_"s"/"e"_"p" = "N"_"s"/"N"_"p"` ….(3)
Equation (3) represents equation of transformer.
The ratio `"N"_"s"/"N"_"p"` is called turns ratio (transformer ratio) of the transformer.
h. For an ideal transformer,
Input power = Output power
∴ ePIP = eSIS
∴ `"e"_"s"/"e"_"p" = "I"_"p"/"I"_"s"` ….(4)
i. From equation (3) and (4),
`"e"_"s"/"e"_"p" = "N"_"s"/"N"_"p" = "I"_"p"/"I"_"s"`
Notes
Students should refer to the answer according to their questions.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the construction and working of the transformer.
Draw a labeled diagram of a step-down transformer.
A group of students while coming from the school noticed a box marked "Danger H.T. 2200 V" at a substation in the main street. They did not understand the utility of a such a high voltage, while they argued, the supply was only 220 V. They asked their teacher this question the next day. The teacher thought it to be an important question and therefore explained to the whole class.
Answer the following questions:
(i) What device is used to bring the high voltage down to low voltage of a.c. current and what is the principle of its working ?
(ii) Is it possible to use this device for bringing down the high dc voltage to the low voltage? Explain
(iii) Write the values displayed by the students and the teacher.
Express the turn ratio in terms of voltages.
Name two factors on which the magnitude of an induced e.m.f. in the secondary coil depends.
The teachers of Geeta’s school took the students on a study trip to a power generating station, located nearly 200 km away from the city. The teacher explained that electrical energy is transmitted over such a long distance to their city, in the form of alternating current (ac) raised to a high voltage. At the receiving end in the city, the voltage is reduced to operate the devices. As a result, the power loss is reduced. Geeta listened to the teacher and asked questions about how the ac is converted to a higher or lower voltage.
1) Name the device used to change the alternating voltage to a higher or lower value. State one cause for power dissipation in this device.
2) Explain with an example, how power loss is reduced if the energy is transmitted over long distances as an alternating current rather than a direct current.
3) Write two values each shown by the teachers and Geeta.
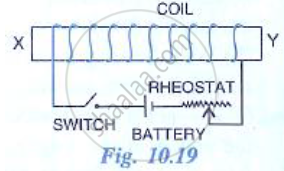
The adjacent diagram shows a coil would around a soft iron bar XY. (a) State the polarity at the end X and Y as the switch is pressed. (b) Suggest one way increasing the strength of electromagnet so formed.
State two factors on which the magnitude of induced e.m.f. depend.
Name the phenomenon ?
Explain why an induced current must flow in such a direction so as to oppose the change producing it.
Explain the significance of Lenz’s law to show the conservation of energy in electromagnetic induction.
Name two kind of energy loss in a transformer. How is it minimized?
The input and output voltage of a transformer are 220 V and 44 V respectively. Find: the turns ratio.
Draw a labeled diagram of a full wave rectifier circuit. State its working principle. Show the input-output waveforms ?
What is the turns ratio i.e., transformer ratio, ns: np, in an ideal transformer which in-creases ac voltage from 220 V to 33000 V?
In an ideal transformer, an output of 66 kV is required when an input voltage of 220 V is available. If the primary has 300 turns, how many turns should the secondary have?
What is a transformer? On what principle does it work?
State the principle of a transformer.
Can a transformer be used with direct current source? Give reason.
Name the principle on which functioning of a transformer depends.
What is the function of a step-up transformer?
Name three losses of energy in a transformer. How are they minimized?
Copy the given diagram of a transformer and complete it. Name the parts A and B. Name the part you have drawn to complete the diagram. What is the material of this part? Is this transformer a step-up or step-down? Give reason.
The power supply to the primary coil of a transformer is 200 W. Find
(i) Current in primary coil if the e.m.f. supply to it is equal to 220V.
(ii) The number of turns in the primary coil is equal to 80 and that in secondary is 800. What is the transformation ratio?
(iii) Name the type of transformer.
(iv) What will be the output voltage?
(v) What is the current in the secondary coil for an ideal transformer?
(vi) What is the output power?
(vii) Is output and input power equal?
(viii) Compare the current flowing in a secondary coil and in a primary coil.
A transformer lowers e.m.f. from 220 V to 15 V. If the number of turns in primary are 3520, how many turns are in the secondary coil?
An ideal transformer has 100 turns in the primary and 250 turns in the secondary. The peak value of the AC is 28 V. The rms secondary voltage is nearest to ______
State the mathematical relation between a number of turns in the primary coil to a secondary coil in the step-up transformer.
Explain step up and step down transformer?
Devices which is used to convert high alternating current to low alternating current is ______.
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
A transformer can step up direct current.
In a series resonant RLC circuit, the voltage across 100 Ω resistor is 40 V. The resonant frequency ω is 250 rad/s. If the value of C is 4 µF, then the voltage across L is
Find out the phase relationship between voltage and current in a pure inductive circuit.
A 200V/120V step-down transformer of 90% efficiency is connected to an induction stove of resistance 40 Ω. Find the current drawn by the primary of the transformer.
Assertion: A transfonner cannot work on D.C. supply.
Reason: D.C. changes neither in magnitude nor in direction.
A power transmission line feeds input power at 2300 V to a stepdown transformer with its primary windings having 4000 turns. What should be the number of turns in the secondary in order to get output power at 230 V?
Which among the following, is not a cause for power loss in a transformer?
Read the following paragraph and answer the question:

Long distance power transmissions
The large-scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped up. It is then transmitted over long distances to an area sub-station near the consumers. There the voltage is stepped down. It is further stepped down at distributing sub-stations and utility poles before a power supply of 240 V reaches our homes.
If the secondary coil has a greater number of turns than the primary, ______.
Read the following paragraph and answer the question:

Long distance power transmissions
The large-scale transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances is done with the use of transformers. The voltage output of the generator is stepped up. It is then transmitted over long distances to an area sub-station near the consumers. There the voltage is stepped down. It is further stepped down at distributing sub-stations and utility poles before a power supply of 240 V reaches our homes.
We need to step-up the voltage for power transmission, so that ______.
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
The value of current in primary coil is ______.
A transformer is essentially an a.c. device. It cannot work on d.c. It changes alternating voltages or currents. It does not affect the frequency of a.c. It is based on the phenomenon of mutual induction. A transformer essentially consists of two coils of insulated copper wire having different numbers of turns and wound on the same soft iron core.
The number of turns in the primary and secondary coils of an ideal transformer is 2000 and 50 respectively. The primary coil is connected to a main supply of 120 V and secondary coil is connected to a bulb of resistance 0.6 Ω.
Power in primary coil is ______.
The primary coil of a transformer has 800 turns and the secondary coil has 8 turns. It is connected to a 220 V ac supply. What will be the output voltage?
The primary winding of a transformer has 100 turns and its secondary winding has 200 turns. The primary is connected to an a.c supply of 120 V and the current flowing in its is 10 A. The voltage and the current in the secondary are ______.
A step-down transformer connected to an ac mains supply of 220 V is made to operate at 11 V, 44 W lamp. Ignoring power losses in the transformer, what is the current in the primary circuit?
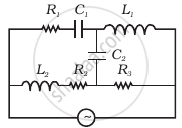
Draw the effective equivalent circuit of the circuit shown in figure, at very high frequencies and find the effective impedance.
1 MW power is to be delivered from a power station to a town 10 km away. One uses a pair of Cu wires of radius 0.5 cm for this purpose. Calculate the fraction of ohmic losses to power transmitted if
- power is transmitted at 220 V. Comment on the feasibility of doing this.
- a step-up transformer is used to boost the voltage to 11000 V, power transmitted, then a step-down transfomer is used to bring voltage to 220 V. (ρCu = 1.7 × 10–8 SI unit)
An ideal transformer converts 220 V a.c. to 3.3 kV a.c. to transmit a power of 4.4 kW. If primary coil has 600 turns, then alternating current in secondary coil is ______.
The primary coil of a transformer has 60 turns whereas its secondary coil has 3000 turns.
If a current of 5A flows in the primary coil, how much current will flow in a load in the secondary coil? State the assumption you have made regarding the transformer, in this calculation.
What is a transformer?
What type of transformer is used in a mobile phone charger?
For what purpose are the transformers used?
