Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Describe the dihybrid cross upto F2 generation as conducted by Gregor Mendel using pure lines of Garden Pea for characters-seed shape and seed colour.
उत्तर
Yellow colour was dominant over green and round shape was dominant over wrinkled. These results were identical to those that he got when he made separate monohybrid crosses between yellow and green-seeded plants and between round and wrinkled-seeded plants. Let us use the genotypic symbols Y for the dominant yellow seed colour and y for the recessive green seed colour, R for round-shaped seeds and r for wrinkled seed shape. The genotype of the parents can then be written as RRYY and rryy. The cross between the two plants can be written down showing the genotypes of the parent plants. The gametes RY and ry unite on fertilisation to produce the F1 hybrid RrYy. When Mendel self-hybridised the F1 plants, he found that 3/4th of F2 plants had yellow seeds and 1/4th had green. The yellow and green colours are segregated in a 3 : 1 ratio. Round and wrinkled seed shapes are also segregated in a 3 : 1 ratio; just like in a monohybrid cross. In the dihybrid cross Figure, the phenotypes round, yellow; wrinkled, yellow; round, green and wrinkled, green appeared in the ratio 9 : 3 : 3 : 1. Such a ratio was observed for several pairs of characters that Mendel studied. The ratio of 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 can be derived as a combination series of 3 yellow : 1 green, with 3 round : 1 wrinkled. This derivation can be written as follows: (3 Round : 1 Wrinkled) (3 Yellow : 1 Green) = 9 Round, Yellow : 3 Wrinkled, Yellow: 3 Round, Green : 1 Wrinkled, Green Based upon such observations on dihybrid crosses (crosses between plants differing in two traits) Mendel proposed a second set of generalisations that we call Mendel’s Law of Independent Assortment. The law states that ‘when two pairs of traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters’.
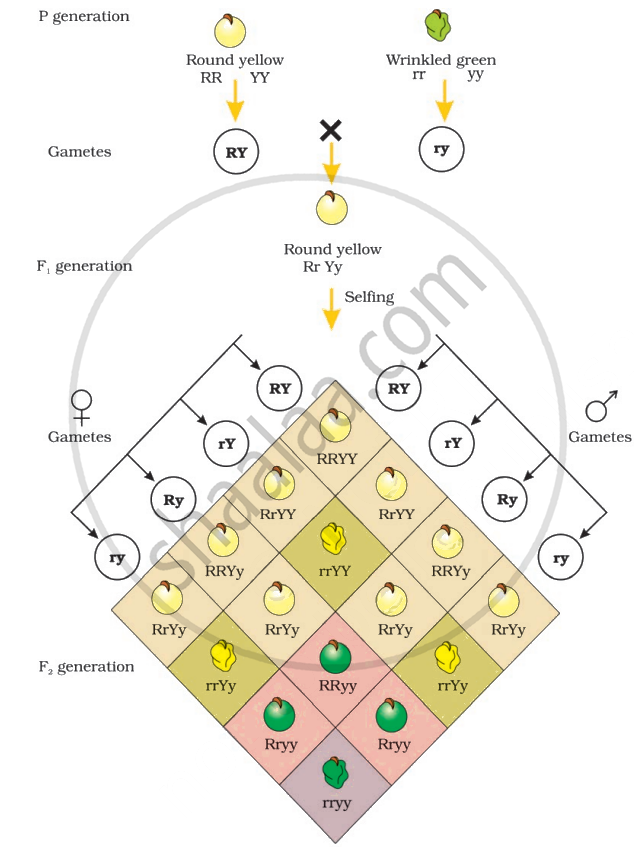
Phenotypic ratio:
| round yellow : round green : wrinkled yellow : wrinkled green |
| 9 3 3 1 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two heterozygous parents are crossed. If the two loci are linked what would be the distribution of phenotypic features in F1 generation for a dihybrid cross?
Filling the blank based on the given relationship.
3 : 1 Monohybrid : : 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 : ______
Under which conditions does the law of independent assortment hold good and why?
The genotype of a plant showing the dominant phenotype can be determined by
In a test cross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental type offspring were produced than the recombination type offspring. This indicates
Name the seven contrasting traits of Mendel.
Findings of Gregor Mendel were rediscovered by the following scientists EXCEPT for ______
In a testcross involving F1 dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant-type offspring. This indicates ______.
Mendel’s last law is ______.
The process of mating between closely related individuals is ______.
Mendel’s Law of independent assortment holds good for genes situated on the ______.
Assertion: When the two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations is much higher than the nonparental type.
Reason: Higher parental gene combinations can be attributed to crossing over between two genes.
According to the evolutionary theory, formation of a new species is generally due to
How is the sex of a newborn determined in humans?
Two pea plants - one with round yellow seeds (RRYY) and another with wrinkled green (rryy) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds.
When F1 plants are self-pollinated, which new combination of characters is expected in F2 progeny? How many seeds with these new combinations of characters will be produced when a total 160 seeds are produced in F2 generation? Explain with reason.
Which of the following statement is not correct for two genes that show 50% recombination frequency?
