Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the conversion of galvanometer into an ammeter and also a voltmeter.
उत्तर
- The ammeter must offer low resistance, no change in current.
- Galvanometer is converted to an ammeter by connecting low resistance in parallel.
- Low resistance – Shunt resistance.
- I – current in the circuit.
- Ig – Galvanometer current.
- Rg – Galvanometer resistance.
- Current through the shunt, Is = I – Ig
- `"V"_"galvanometer" = "V"_"shunt"`
Ig Rg = (I – Ig)S
S = `("I"_"g" "R"_"g")/("I - I"_"g")` .....(1)
`"I"_"g" = "S"/("S" + "R"_"g")"I"`
Ig α I
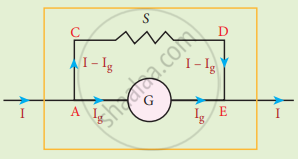
Ammeter
The deflection in the galvanometer is proportional to current θ α Ig
`1/"R"_"eff" = 1/"R"_"g" + 1/"s"`
`1/"R"_"eff" = ("R"_"g""S")/("R"_"g" + "S") = "R"_"a"`
Ra is very low.
An ideal ammeter has zero resistance.
Galvanometer to a voltmeter:
- The voltmeter must have high resistance.
- A galvanometer is converted to a voltmeter by connecting high resistance in series.
- Rg – Galvanometer resistance.
- Ig – Galvanometer current.
- Rh – High resistance
- Since it is connected in series, the current is the same.
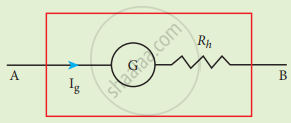
Voltmeter
i.e. I = Ig
`"I"_"g" = "Potential difference"/"total resistance"`
Rv = Rg + Rh
`"I"_"g" = "V"/("R"_"g" + "R"_"h")`
`"R"_"h" = "V"/"I"_"g" - "R"_"g"`
∴Ig α V - An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Biot-Savart’s law.
How is a galvanometer converted into
- an ammeter and
- a voltmeter?
Deduce the relation for the magnetic induction at a point due to an infinitely long straight conductor carrying current.
Obtain a relation for the magnetic induction at a point along the axis of a circular coil carrying current.
What is tangent law? Discuss in detail.
