Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Discuss the following case-
Observer in motion and Source at rest.
- Observer moves towards Source
- Observer resides away from the Source
उत्तर
(a) Observer moves towards Source:
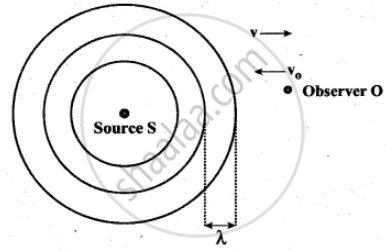
Observer moves towards Source
We can assume that the observer O moves towards the source S with velocity vo. The source S is at rest and the velocity of sound waves (with respect to the medium) produced by the source is v.
From the Figure, It is observed that both vo and v are in opposite direction. Then, their relative velocity is vr = v + vo. The wavelength of the sound wave is λ = `"v"/"f"`, which means the frequency observed by the observer O is f ‘ = `"v"_"r"/lambda`. Then
`"f"' = "v"_"r"/lambda = (("v" + "v"_0)/"v")"f"`
`= "f"(1 + "v"_0/"v")` ...(7)
(b) Observer recedes away from the Source:
If the observer O is moving away (receding away) from the source S, then velocity v0 and v move in the same direction. Hence, their relative velocity is vr = v – v0. Hence, the frequency observed by the observer O is
`"f"' = "v"_"r"/lambda = (("v" + "v"_0)/"v")"f"`
`= "f"(1 - "v"_0/"v")` ...(8)
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Answer briefly.
State the expression for apparent frequency when source of sound and listener are
- moving towards each other
- moving away from each other
Solve the following problem.
A police car travels towards a stationary observer at a speed of 15 m/s. The siren on the car emits a sound of frequency 250 Hz. Calculate the recorded frequency. The speed of sound is 340 m/s.
A ship in a sea sends SONAR waves straight down into the seawater from the bottom of the ship. The signal reflects from the deep bottom bedrock and returns to the ship after 3.5 s. After the ship moves to 100 km it sends another signal which returns back after 2 s. Calculate the depth of the sea in each case and also compute the difference in height between two cases.
N tuning forks are arranged in order of increasing frequency and any two successive tuning forks give n beats per second when sounded together. If the last fork gives double the frequency of the first (called as octave), Show that the frequency of the first tuning fork is f = (N – 1)n.
How do animals sense impending danger of hurricane?
A bus is moving with a velocity of 5 m is towards a wall. The driver blows the horn of frequency 165 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 335 m is, then after reflection of sound wave, the number of beats per second heard by the passengers in the bus will be ______.
A train, standing in a station yard, blows a whistle of frequency 400 Hz in still air. The wind starts blowing in the direction from the yard to the station with a speed of 10 m/s. Given that the speed of sound in still air is 340 m/s ______.
- the frequency of sound as heard by an observer standing on the platform is 400 Hz.
- the speed of sound for the observer standing on the platform is 350 m/s.
- the frequency of sound as heard by the observer standing on the platform will increase.
- the frequency of sound as heard by the observer standing on the platform will decrease.
In a quink tube experiment, a tuning fork of frequency 300 Hz is vibrated at one end. It is observed that intensity decreases from maximum to 50% of its maximum value, as tube is moved by 6.25 cm. Velocity of sound is ______ m/s.
When a sound source of frequency n is approaching a stationary observer with velocity u than the apparent change in frequency is Δn1 and when the same source is receding with velocity u from the stationary observer than the apparent change in frequency is Δn2. Then ______.
The observer is moving with velocity 'v0' towards the stationary source of sound and then after crossing moves away from the source with velocity 'v0'. Assume that the medium through which the sound waves travel is at rest. If v is the velocity of sound and n is the frequency emitted by the source, then the difference between apparent frequencies heard by the observer is ______.
