Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the following case-
Observer in motion and Source at rest.
- Observer moves towards Source
- Observer resides away from the Source
Solution
(a) Observer moves towards Source:
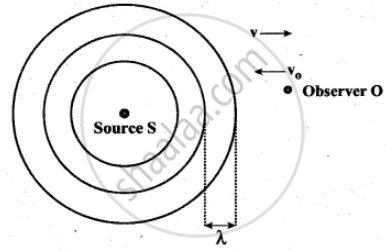
Observer moves towards Source
We can assume that the observer O moves towards the source S with velocity vo. The source S is at rest and the velocity of sound waves (with respect to the medium) produced by the source is v.
From the Figure, It is observed that both vo and v are in opposite direction. Then, their relative velocity is vr = v + vo. The wavelength of the sound wave is λ = `"v"/"f"`, which means the frequency observed by the observer O is f ‘ = `"v"_"r"/lambda`. Then
`"f"' = "v"_"r"/lambda = (("v" + "v"_0)/"v")"f"`
`= "f"(1 + "v"_0/"v")` ...(7)
(b) Observer recedes away from the Source:
If the observer O is moving away (receding away) from the source S, then velocity v0 and v move in the same direction. Hence, their relative velocity is vr = v – v0. Hence, the frequency observed by the observer O is
`"f"' = "v"_"r"/lambda = (("v" + "v"_0)/"v")"f"`
`= "f"(1 - "v"_0/"v")` ...(8)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain red shift and blue shift in Doppler Effect.
What is meant by the Doppler effect?
N tuning forks are arranged in order of increasing frequency and any two successive tuning forks give n beats per second when sounded together. If the last fork gives double the frequency of the first (called as octave), Show that the frequency of the first tuning fork is f = (N – 1)n.
The difference between the apparent frequency of a source of sound as perceived by the observer during its approach and recession is 2% of the frequency of the source. If the speed of sound in air is 300 ms-1, then the velocity of the source is ______.
A bus is moving with a velocity of 5 m is towards a wall. The driver blows the horn of frequency 165 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 335 m is, then after reflection of sound wave, the number of beats per second heard by the passengers in the bus will be ______.
An observer moves towards a stationary source of sound with a velocity one-fifth of the velocity of sound. The percentage increase in the apparent frequency heard by the observer will be ______.
A car sounding a horn of frequency 1000 Hz passes au observer. The ratio of frequencies of the horn noted by the observer before and after passing of the car is 11 : 9. If the speed of sound is 'V', the speed of the car is ______.
A train moving at 25 m/s emits a whistle of frequency 200 Hz. If the speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, find the frequency observed by a stationary observer.
- if the observer is in front of the source.
- if the observer is behind the train.
A whistle producing sound waves of frequencies 9500 Hz and above is approaching a stationary person with speed v ms-1. The velocity of sound in air is 300 ms-1. If the person can hear frequencies up to a maximum of 10,000 HZ, the maximum value of v up to which he can hear the whistle is ______.
The pitch of the whistle of an engine appears to drop by 20% of its original value when it passes a stationary observer. If the speed of sound in the air is 350 m/s, then the speed of the engine (in m/s) is ______.
