Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Distinguish between SN1 and SN2 mechanism of substitution reaction.
उत्तर
| Factor | SN1 | SN2 |
| Kinetics | 1st order | 2nd order |
| Molecularity | Unimolecular | Bimolecular |
| Number of steps | Two steps | One step |
| Bond making and bond breaking | First the bond in the reactant breaks and then a new bond in the product is formed. | Simultaneous |
| Transition state | Two steps, two transition states | One step, one transition state |
| Direction of attack of nucleophile | Back side attack and front side attack | Only back side attack |
| Stereochemistry | Racemisation (If the substrate is optically active) | Inversion of configuration (If the substrate is optically active) |
| Type of substrate | Mainly 3° substrates | Mainly 1° substrate |
| Polarity of solvent | Polar protic solvent favorable | Aprotic (non-polar) or solvent with low polarity favourable |
| Intermediate | Intermediate involved | No intermediate |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
from the following pair would undergo SN2 faster from the other?
a. ![]() b.
b. ![]()
Complete the following reaction giving major products.
\[\ce{CH3 - CH = CH2 ->[HBr][peroxide] A ->[alc. KOH] B}\]
Complete the following reaction giving major products.

Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
1-Chloropropane to 1-nitropropane
Name the reagent used to bring about the following conversion.
Ethyl bromide to ethyl isocyanide
Arrange the following in the increasing order of boiling points.
- 1-Bromopropane
- 2- Bromopropane
- 1- Bromobutane
- 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane
Convert the following:
Propene to propan-1-ol
Observe the following and answer the question given below.

Name the type of halogen derivative.
Observe the following and answer the question given below.

Comment on the bond length of C–X bond in it.
Major product of the following reaction is _______________
\[\ce{CH3-CH2-Mg-Br + NH3 ->?}\]
Explain. Aryl halides are less reactive than alkyl halides towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Explain primary benzylic halide shows higher reactivity by SN1 mechanism than other primary alkyl halide.
Explain the factors affecting SN1 and SN2 mechanism.
Explain aqueous alkaline hydrolysis of tert. butyl bromide.
Ethyl bromide undergoes the following reaction:
\[\ce{\underset{Ethyl bromide}{C2H5Br} + \underset{(aq.)}{KOH} ->[\Delta] \underset{Ethyl alcohol}{C2H5OH} + KBr}\]
Which of the following is a WRONG statement?
Nitroalkanes are obtained in laboratory from primary or secondary alkyl halides by the action of ______.
Identify major product 'B' in the following reaction.
\[\ce{But-1-ene ->[HBr][Peroxide] A ->[AgCN][\Delta] B}\]
Write the product formed when alkyl halide reacts with silver nitrite.
Convert the following.
p-Nitrochlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
The order of reactivities of the following alkyl halides for an SN2 reaction is ______.
Which among the following statements is not correct about SN2 reaction mechanism?
The compound that reacts the fastest with sodium methoxide is ______.
Explain the dehydrohalogenation reaction of 2-chlorobutane.
Observe the following and answer the questions given below:
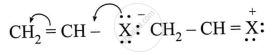
Name the type of halogen derivative.
Observe the following and answer the question given below:
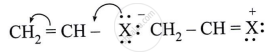
Can react by SN1 mechanism? Justify your answer.
Identify the chiral molecule from the following.
Complete the following reaction giving major product.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3 - C - CH2 - Cl ->[Na/dry ether] A}\\
|\phantom{...................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}\\
\end{array}\]
