Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Do the same with the replacement of the earlier transformer by a 40,000-220 V step-down transformer (Neglect, as before, leakage losses though this may not be a good assumption any longer because of the very high voltage transmission involved). Hence, explain why high voltage transmission is preferred?
उत्तर
The rating of a step-down transformer is 40000 V − 220 V.
Input voltage, V1 = 40000 V
Output voltage, V2 = 220 V
Total electric power required, P = 800 kW = 800 × 103 W
Source potential, V = 220 V
Voltage at which the electric plant generates power, V‘ = 440 V
Distance between the town and power generating station, d = 15 km
Resistance of the two wire lines carrying power = 0.5 Ω/km
Total resistance of the wire lines, R = (15 + 15) 0.5 = 15 Ω
P = V1I
Rms current in the wire line is given as:
I = `"P"/"V"_1`
= `(800 xx 10^3)/40000`
= 20 A
(a) Line power loss = I2R
= (20)2 × 15
= 6 kW
(b) Assuming that the power loss is negligible due to the leakage of current.
Hence, power supplied by the plant = 800 kW + 6kW = 806 kW
(c) Voltage drop in the power line = IR = 20 × 15 = 300 V
Hence, voltage that is transmitted by the power plant
= 300 + 40000 = 40300 V
The power is being generated in the plant at 440 V.
Hence, the rating of the step-up transformer needed at the plant is 440 V − 40300 V.
Hence, power loss during transmission = `600/1400 xx 100` = 42.8%
In the previous exercise, the power loss due to the same reason is `6/806 xx 100` = 0.744%. Since the power loss is less for a high voltage transmission, high voltage transmissions are preferred for this purpose.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The given graph shows the variation of photo-electric current (I) versus applied voltage (V) for two difference photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but same intensity of incident radiation.
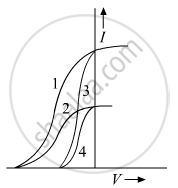
In a series LCR circuit connected to an ac source of variable frequency and voltage ν = vm sin ωt, draw a plot showing the variation of current (I) with angular frequency (ω) for two different values of resistance R1 and R2 (R1 > R2). Write the condition under which the phenomenon of resonance occurs. For which value of the resistance out of the two curves, a sharper resonance is produced? Define Q-factor of the circuit and give its significance.
The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by V = V0cos ωt and i = i0 sin ωt. What is the power dissipated in the circuit?
An alternating current of peak value 14 A is used to heat a metal wire. To produce the same heating effect, a constant current i can be used, where i is
The household supply of electricity is at 220 V (rms value) and 50 Hz. Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero.
An electric bulb is designed to operate at 12 volts DC. If this bulb is connected to an AC source and gives normal brightness, what would be the peak voltage of the source?
Answer the following question.
A small town with a demand of 1200 kW of electric power at 220 V is situated 20 km away from an electric plant generating power at 440 V. The resistance of the two wirelines carrying power is 0.5 Ω per km. The town gets the power from the line through a 4000-220 V step-down transformer at a sub-station in the town. Estimate the line power loss in the form of heat.
Phase diffn between voltage and current in a capacitor in A.C Circuit is.
RMS value of an alternating current flowing in a circuit is 5A. Calculate its peak value.
In the Figure below, the current-voltage graphs for a conductor are given at two different temperatures, T1 and T2.
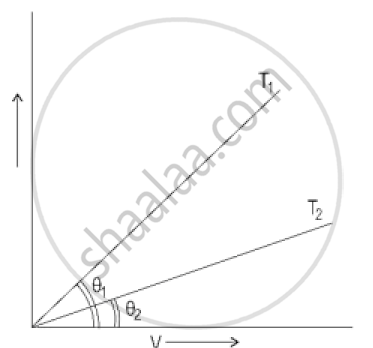
- At which temperature T1 or T2 is the resistance higher?
- Which temperature (T1 or T2) is higher?
