Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A small town with a demand of 800 kW of electric power at 220 V is situated 15 km away from an electric plant generating power at 440 V. The resistance of the two wire line carrying power is 0.5 Ω per km. The town gets power from the line through a 4000-220 V step-down transformer at a sub-station in the town.
(a) Estimate the line power loss in the form of heat.
(b) How much power must the plant supply, assuming there is negligible power loss due to leakage?
(c) Characterise the step up transformer at the plant.
उत्तर
Total electric power required, P = 800 kW = 800 × 103 W
Supply voltage, V = 220 V
Voltage at which electric plant is generating power, V' = 440 V
Distance between the town and power generating station, d = 15 km
Resistance of the two wire lines carrying power = 0.5 Ω/km
Total resistance of the wires, R = (15 + 15) 0.5 = 15 Ω
A step-down transformer of rating 4000 − 220 V is used in the sub-station.
Input voltage, V1 = 4000 V
Output voltage, V2 = 220 V
Rms current in the wire lines is given as:
I = `"P"/"V"_1`
= `(800 xx 10^3)/4000`
= 200 A
(a) Line power loss = I2R
= (200)2 × 15
= 600 × 103 W
= 600 kW
(b) Assuming that the power loss is negligible due to the leakage of the current:
Total power supplied by the plant = 800 kW + 600 kW
= 1400 kW
(c) Voltage drop in the power line = IR = 200 × 15 = 3000 V
Hence, total voltage transmitted from the plant
= 3000 + 4000
= 7000 V
Also, the power generated is 440 V.
Hence, the rating of the step-up transformer situated at the power plant is 440 V − 7000 V.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
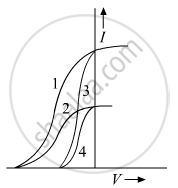
The given graph shows the variation of photo-electric current (I) versus applied voltage (V) for two difference photosensitive materials and for two different intensities of the incident radiations. Identify the pairs of curves that correspond to different materials but same intensity of incident radiation.
The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by V = V0cos ωt and i = i0 sin ωt. What is the power dissipated in the circuit?
Two alternating currents are given by `i_1 = i_0 sin wt and i_2 = i_0 sin (wt + pi/3)` Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different?
An alternating current is given by i = i1 cos ωt + i2 sin ωt. The rms current is given by
A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The rms current is
The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m. A parallel-plate air-capacitor has area 20 cm2 and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source that can be safely connected to this capacitor.
A capacitor of capacitance 10 μF is connected to an oscillator with output voltage ε = (10 V) sin ωt. Find the peak currents in the circuit for ω = 10 s−1, 100 s−1, 500 s−1 and 1000 s−1.
The rms value of current in an ac circuit is 10 A. What is the peak current?
Do the same with the replacement of the earlier transformer by a 40,000-220 V step-down transformer (Neglect, as before, leakage losses though this may not be a good assumption any longer because of the very high voltage transmission involved). Hence, explain why high voltage transmission is preferred?
The period of oscillation of a simple pendulum is T = `2π sqrt"L"/"g"`. The measured value of L is 20.0 cm known to have 1 mm accuracy and the time for 100 oscillations of the pendulum is found to be 90 s using a wristwatch of ls resolution. The accuracy in the determination of g is:
